Associations of TG/HDL Ratio with the Risk of Prediabetes and Diabetes in Chinese Adults: A Chinese Population Cohort Study Based on Open Data
- PMID: 34306073
- PMCID: PMC8282372
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9949579
Associations of TG/HDL Ratio with the Risk of Prediabetes and Diabetes in Chinese Adults: A Chinese Population Cohort Study Based on Open Data
Abstract
Background: In the global chronic diseases, type 2 diabetes shows a significant upward trend, and there are more people before prediabetes (impaired glucose tolerance). Many patients with impaired glucose tolerance and undiagnosed diabetes do not know that their glucose metabolism system has been in a state of disorder. Every year, about 5% to 10% of prediabetics develop diabetes. One of the important achieving factors may be the increase in blood lipids. However, it is not clear whether the triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein ratio is associated with impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes in the Chinese population. Therefore, we investigated the relationship between triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein and impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes in the Chinese population.
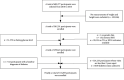
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the health screening program. The study included 116,855 participants from 32 locations in China, all of whom were adults over 20. Participants measured fasting blood glucose levels at each visit and collected information about their diabetes history. Impaired glucose tolerance was diagnosed as fasting blood glucose ≥6.00 mmol and self-reported diabetes mellitus. The patient was measured on the date of diagnosis or on his last visit (whichever comes first).
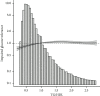
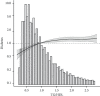
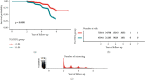
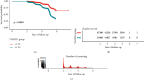
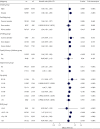
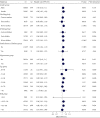
Results: The results showed that, after adjusting the potential confounding factors, the ratio of TG/HDL was positively correlated with the occurrence of prediabetes and diabetes, and there was a saturation effect. The inflection points were 1.04 and 1.33, respectively. The effect value and 95% confidence interval before and after the inflection point of impaired glucose tolerance patients were 1.57 and (1.42, 1.73) and 1.03 and (1.01, 1.05), respectively. The effect value and 95% confidence interval before and after the inflection point in patients with diabetes were 2.07 and (1.80, 2.39) and 1.08 and (1.04, 1.12).
Copyright © 2021 Rongpeng Gong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and incident of diabetes mellitus: a secondary retrospective analysis based on a Chinese cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Mar 4;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01213-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32131838 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the risk factors associated with prediabetes in normal-weight Qatari adults: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 4;14(1):23116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73476-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39367088 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic values and appropriate cutoff points of lipid ratios in patients with abnormal glucose tolerance status: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jun 1;18(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1070-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31153374 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of diabetes and prediabetes on the short-term prognosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Sep 15;332(1-2):45-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23810779
-
Serum γ-glutamyltransferase and uric acid levels are associated with impaired fasting glucose in adults from Inner Mongolia, China.BMC Public Health. 2013 Apr 3;13:294. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-294. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23552170 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Visceral Adiposity Index and Insulin Resistance: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on US Adults.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;13:921067. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.921067. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35937809 Free PMC article.
-
From normal population to prediabetes and diabetes: study of influencing factors and prediction models.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 26;14:1225696. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1225696. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37964953 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and mortality in Chinese maintenance haemodialysis patients: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Apr 10;14(4):e078981. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078981. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38604629 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Magnesium Intake Level Modifies the Association Between Vitamin D and Insulin Resistance: A Large Cross-Sectional Analysis of American Adults.Front Nutr. 2022 Jun 7;9:878665. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.878665. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35747262 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio as a risk factor for progression to prediabetes: a 5-year retrospective cohort study in Japan.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Oct 25;23(1):655-664. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01329-8. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932848 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

