Study on HOXBs of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Detection of New Molecular Target
- PMID: 34306077
- PMCID: PMC8282400
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5541423
Study on HOXBs of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Detection of New Molecular Target
Abstract
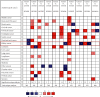
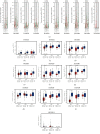
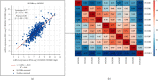
Our study examined the transcriptional and survival data of HOXBs in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) from the ONCOMINE database, Human Protein Atlas, and STRING website. We discovered that the expression levels of HOXB3/5/6/8/9 were significantly lower in ccRCC than in normal nephritic tissues. In ccRCC, patients with a high expression of HOXB2/5/6/7/8/9 mRNA have a higher overall survival (OS) than patients with low expression. Further analysis by the GSCALite website revealed that the methylation of HOXB3/5/6/8 in ccRCC was significantly negatively correlated to gene expression, while HOXB5/9 was positively correlated to the CCT036477 drug target. As DNA abnormal methylation is one of the mechanisms of tumorigenesis, we hypothesized that HOXB5/6/8/9 are potential therapeutic targets for patients with ccRCC. We analyzed the function of enrichment data of HOXBs in patients with ccRCC from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment and the PANTHER pathway. The results of the analysis show that the function of HOXBs might be associated with the Wnt pathway and that HOXB5/6/8/9 was coexpressed with multiple Wnt pathway classical genes and proteins, such as MYC, CTNNB, Cyclin D1 (CCND1), and tumor protein P53 (TP53), which further confirms that HOXBs inhibit the growth of renal carcinoma cells through the Wnt signaling pathway. In conclusion, our analysis of the family of HOXBs and their molecular mechanism may provide a theoretical basis for further research.
Copyright © 2021 Guangzhen Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Caspase 4 Overexpression as a Prognostic Marker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Study Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas Data Mining.Front Genet. 2021 Jan 14;11:600248. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.600248. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33584797 Free PMC article.
-
SOX6 represses tumor growth of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by HMG domain-dependent regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Oct;59(10):1159-1173. doi: 10.1002/mc.23246. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 32794610
-
Overexpression of FZD1 is Associated with a Good Prognosis and Resistance of Sunitinib in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2019 Jan 29;10(5):1237-1251. doi: 10.7150/jca.28662. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30854133 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Through AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):891-904. doi: 10.1159/000491957. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30032137
-
Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jul;39(7):1010428317711314. doi: 10.1177/1010428317711314. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28718366
Cited by
-
The Diagnostic Value of Serum Ang, VEGF, and CRP Combined with the Chinese Medicine Antitumor Formula in the Treatment of Advanced Renal Carcinoma.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 14;2021:5189069. doi: 10.1155/2021/5189069. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34950214 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis revealed a novel nine-gene prognostic risk score of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 27;103(39):e39678. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039678. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39331921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer R. J., Barrios C. H., Kim T. M., et al. Phase II randomized trial comparing sequential first-line everolimus and second-line sunitinib versus first-line sunitinib and second-line everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2014;32(25):2765–2772. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.54.6911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choueiri T. K., Figueroa D. J., Fay A. P., et al. Correlation of PD-L1 tumor expression and treatment outcomes in patients with renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib or pazopanib: results from COMPARZ, a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Cancer Research. 2015;21(5):1071–1077. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-1993. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

