The effect of Wuqinxi exercises on the balance function and subjective quality of life in elderly, female knee osteoarthritis patients
- PMID: 34306416
- PMCID: PMC8290749
The effect of Wuqinxi exercises on the balance function and subjective quality of life in elderly, female knee osteoarthritis patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the balance function and subjective quality of life in elderly female knee osteoarthritis patients KOAKOA treated with Wuqinxi exercises.
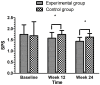
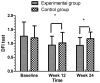
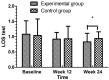
Methods: A total of 284 elderly female patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) were randomly divided into an experimental group, which did Wuqinxi exercises for 24-weeks (n=132), and a control group, which didn't do any regular physical exercises (n=134). The experimental group did Wuqinxi exercises for 24 weeks, and the control group didn't engage in any regular physical exercise. We performed limits of stability (LOS) tests, static posture stability (SPS) tests, and dynamic fall index (DFI) tests to assess the patients' balance, and we administered the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) questionnaire to evaluate the physical functioning of the patients' knees.
Results: The limits of stability (LOS) test, the static posture stability (SPS) test, and the dynamic fall index (DFI) test results were improved in the experimental group compared with the control group (P < 0.05). From baseline to the week 24 follow-up, the WOMAC tests, and the pain, joint stiffness, and lower limb muscle strength showed significant differences between the two groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Wuqinxi exercises are an effective treatment for elderly female patients with knee osteoarthritis, and can improve their balance and subjective quality of life. The therapy effectively alleviates the clinical symptoms of the elderly female knee osteoarthritis patients.
Keywords: Wuqinxi exercise; balance function; knee osteoarthritis; quality of life.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Knoop J, van der Leeden M, van der Esch M, Thorstensson CA, Gerritsen M, Voorneman RE, Lems WF, Roorda LD, Dekker J, Steultjens MP. Association of lower muscle strength with self-reported knee instability in osteoarthritis of the knee: results from the Amsterdam Osteoarthritis cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:38–45. - PubMed
-
- Skou ST, Wrigley TV, Metcalf BR, Hinman RS, Bennell KL. Association of knee confidence with pain, knee instability, muscle strength, and dynamic varus-valgus joint motion in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2014;66:695–701. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources