Odontogenic Myxoma: Follow-Up of 13 cases after conservative surgical treatment and review of the literature
- PMID: 34306525
- PMCID: PMC8291164
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.58080
Odontogenic Myxoma: Follow-Up of 13 cases after conservative surgical treatment and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: We aim to report a serie of odontogenic myxoma over a 40-year period.
Material and methods: We conducted a retrospective and sectional review of OM cases. The clinical, radiographic and treatment data were collected from clinical records included cases whose medical records contained clinical, radiographic, histopathological, follow-up data of at least six months.
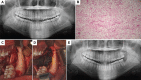
Results: There was a mild preference for the male with a mean age of 22.8 years. Seventy-seven percent of the lesions occurred in the posterior region of the mandible, presenting a multilocular radiolucent aspect (54%) with one presenting symptomatology. Conservative treatment was performed in all patients initially and recurrence was observed in two cases.
Conclusions: Odontogenic myxoma has a well-defined clinical profile and the choice of treatment should consider aspects such as patient's age, lesion size, and location. Key words:Myxoma, odontogenic tumors, diagnosis, treatment.
Copyright: © 2021 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest Author Hélder Domiciano Dantas Martins declares that he has no conflict of interest/ Author Etiana Lopes Vieira declares that she has no conflict of interest/ Author Haroldo Abuana Osório-Júnior declares that he has no conflict of interest/ Author André Luiz Marinho Falcão Gondim declares that he has no conflict of interest/ Author José Sandro Pereira da Silva declares that he has no conflict of interest/ Author Éricka Janine Dantas da Silveira declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathologic analysis of 14 cases of odontogenic myxoma and review of the literature.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):e560-e563. doi: 10.4317/jced.52953. eCollection 2017 Apr. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017. PMID: 28469823 Free PMC article.
-
Odontogenic myxoma--a case report and clinico-radiographic study of seven tumors.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2006 Feb 15;7(1):117-24. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2006. PMID: 16491154
-
Odontogenic Myxoma: Systematic review and bias analysis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2020 Apr;50(4):e13214. doi: 10.1111/eci.13214. Epub 2020 Mar 14. Eur J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32048275
-
[Odontogenic myxoma: About four cases and review of the literature].Ann Pathol. 2010 Jun;30(3):168-75. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2010.03.002. Ann Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20621593 Review. French.
-
Odontogenic myxoma: An updated analysis of 1,692 cases reported in the literature.Oral Dis. 2019 Apr;25(3):676-683. doi: 10.1111/odi.12875. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Oral Dis. 2019. PMID: 29683236 Review.
Cited by
-
Diode laser on excision of giant peripheral odontogenic myxoma: a rare case report and literature review.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Jan 11;38(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03705-5. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36630018 Review.
-
Rehabilitation of a patient with extensive odontogenic myxoma treated conservatively: A case report with 14 years of follow-up.J Clin Exp Dent. 2025 Apr 1;17(4):e488-e492. doi: 10.4317/jced.62679. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Clin Exp Dent. 2025. PMID: 40375841 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative Management of Odontogenic Fibromyxoma of the Maxilla: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 May 6;16(5):e59763. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59763. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38846229 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological and Molecular Features of Odontogenic Myxoma: A Systematic Review.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Jul;77(7):2711-2718. doi: 10.1007/s12070-025-05552-y. Epub 2025 May 16. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40503128
-
Surgical management of odontogenic myxomas: A case series.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Nov;112:108945. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108945. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37913665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siriwardena BSMS, Tennakoon TMPB, Tilakaratne WM. Relative frequency of odontogenic tumors in Sri Lanka: Analysis of 1677 cases. Pathol Res Pr. 2012;208:225–30. - PubMed
-
- Thoma KH, Goldman HM. Central myxoma of the jaw. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1947;33:B532–40. - PubMed
-
- El-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, Takata T, Slootweg PJ. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours. 4th ed. Lyon: 2017.
-
- Chrcanovic BR, Gomez RS. Odontogenic myxoma: An updated analysis of 1,692 cases reported in the literature. Oral Dis. 2019;25:676–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
