Optimized Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm-Based Coronal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanning in Tracheal Foreign Bodies of Children
- PMID: 34306593
- PMCID: PMC8279863
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5678994
Optimized Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm-Based Coronal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanning in Tracheal Foreign Bodies of Children
Abstract
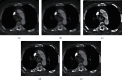
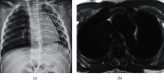
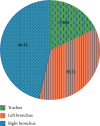
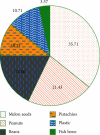
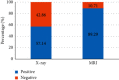
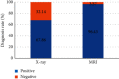
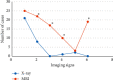
In order to provide theoretical support for clinical diagnosis, the diagnostic value of the optimized fuzzy C-means (FCM) algorithm combined with coronal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan was investigated in the diagnosis of tracheal foreign bodies in children. The anisotropic filtering was applied to optimize the traditional FCM algorithm, so as to construct a new MRI image segmentation algorithm, namely, AFFCM algorithm. Then, the traditional FCM algorithm, the FCM algorithm based on the kernel function (KFCM), and the FCM algorithm based on the spatial neighborhood information (RFCM) were introduced for comparison with the AFFCM. 28 children diagnosed with foreign bodies in the trachea were selected for MRI diagnosis, and AFFCM was used for segmentation. The partition coefficient, segmentation entropy, and the correlation degree between classes after fuzzy division of the four algorithms were recorded, and the location and distribution of foreign bodies in the trachea and the types of foreign bodies were also collected. Besides, the MRI scanning and chest X-rays of the children with foreign bodies in the trachea should also be recorded in terms of the positive rate, diagnosis rate, and indirect signs. The class division coefficient and interclass correlation degree after fuzzy division of AFFCM were markedly greater than those of FCM, KFCM, and RFCM (P < 0.05), while the segmentation entropy of AFFCM was less sharp than the entropies of FCM, KFCM, and RFCM (P < 0.05). Among the 28 children, there were 5 cases with foreign bodies in the trachea (17.86%), 10 cases in the left bronchus (35.71%), and 13 cases in the right bronchus (46.43%). Among the foreign body types, there were 10 cases of melon seeds (35.71%), 6 cases of peanuts (21.43%), and 5 cases of beans (17.86%). The positive rate (89.29%) and diagnosis rate (96.43%) of MRI for bronchial foreign bodies increased obviously in contrast to the rates of X-ray chest radiographs (57.14% and 67.86%) (P < 0.05). Therefore, it was indicated that AFFCM showed higher partition coefficient value, lower segmentation entropy, larger similarity among classes, and better image segmentation effect. Furthermore, AFFCM-based coronal MRI scan had a higher positive rate and diagnosis rate for children's tracheal foreign bodies, and the main signs were emphysema and atelectasis.
Copyright © 2021 Lan Jin and Ke Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel kernelized fuzzy C-means algorithm with application in medical image segmentation.Artif Intell Med. 2004 Sep;32(1):37-50. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2004.01.012. Artif Intell Med. 2004. PMID: 15350623
-
Suspicious Lesion Segmentation on Brain, Mammograms and Breast MR Images Using New Optimized Spatial Feature Based Super-Pixel Fuzzy C-Means Clustering.J Digit Imaging. 2019 Apr;32(2):322-335. doi: 10.1007/s10278-018-0149-9. J Digit Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30402671 Free PMC article.
-
A multiple-kernel fuzzy C-means algorithm for image segmentation.IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern. 2011 Oct;41(5):1263-74. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2124455. Epub 2011 Apr 5. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern. 2011. PMID: 21803693
-
Recent Advancements in Fuzzy C-means Based Techniques for Brain MRI Segmentation.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(8):917-930. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666210104111218. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33397241 Review.
-
Fuzzy C-Means Clustering: A Review of Applications in Breast Cancer Detection.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Jul 4;25(7):1021. doi: 10.3390/e25071021. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Nursing Intervention of Gynecological Ovarian Endometriosis with Magnetic Resonance Imaging under Artificial Intelligence Algorithm.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 11;2022:3123310. doi: 10.1155/2022/3123310. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35726287 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Value of Magnetic Resonance Images and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Diagnosis of Brain Tumors under Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 May 30;2022:3315121. doi: 10.1155/2022/3315121. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35685667 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Deep Learning-Based CT Feature for Severe Pulmonary Infection.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Nov 26;2021:5359084. doi: 10.1155/2021/5359084. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34868521 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

