Idiopathic pulmonary vein thrombosis treated with apixaban
- PMID: 34306707
- PMCID: PMC8292945
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.803
Idiopathic pulmonary vein thrombosis treated with apixaban
Abstract
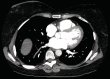
Pulmonary vein thrombosis (PVT) is a rare clinical finding that is potentially fatal and with an unknown incidence rate as known cases exist predominantly in case reports. We present the case of a 58-year-old female who reported sudden onset of chest pain, shortness of breath, and dyspnoea on exertion. A computed tomography (CT) pulmonary angiogram was negative for evidence of pulmonary embolism; however, it did demonstrate the evidence of thrombosis of the right lower lobe segmental pulmonary vein. She had no identifiable aetiologies for her PVT; therefore, she was diagnosed with idiopathic PVT and was treated successfully with apixaban. This case represents the 14th incidence of idiopathic PVT in the current body of medical literature and the first case of successful treatment with apixaban.
Keywords: Apixaban; breast cancer; idiopathic; pulmonary vein thrombosis; venous thrombosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander GR, Reddi A, and Reddy D. 2009. Idiopathic pulmonary vein thrombosis: a rare cause of massive hemoptysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 88(1):281–283. - PubMed
-
- Selvidge SD, and Gavant ML. 1999. Idiopathic pulmonary vein thrombosis: Detection by CT and MR imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 172(6):1639–1641. - PubMed
-
- Mumoli N, and Cei M. 2012. Idiopathic pulmonary vein thrombosis. J. Emerg. Med. 42(2):182–183. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources