Enantioselective, Aerobic Copper-Catalyzed Intramolecular Carboamination and Carboetherification of Unactivated Alkenes
- PMID: 34306802
- PMCID: PMC8293922
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c02607
Enantioselective, Aerobic Copper-Catalyzed Intramolecular Carboamination and Carboetherification of Unactivated Alkenes
Abstract
Reduction of waste is an important goal of modern organic synthesis. We report herein oxidase reactivity for enantioselective intramolecular copper-catalyzed alkene carboamination and carboetherification reactions where previously used stoichiometric MnO2 has been replaced with oxygen. This substitution was risky as the reaction mechanism is thought to involve C-C bond formation via addition of alkyl carbon radicals to arenes. Such intermediates are also susceptible to C-O bond formation via O2 addition. Control of absolute stereochemistry under aerobic conditions was also uncertain. The oxidative cyclization efficiencies appear to track with the ease of the radical addition to the arenes.
Keywords: aerobic oxidation; alkene; asymmetric catalysis; carboamination; carboetherification; copper.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
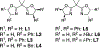


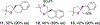
References
-
- Cavani F; Teles JH Sustainability in catalytic oxidation: an alternative approach or a structural evolution? ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 508–534. - PubMed
-
- Caron S; Dugger RW; Ruggeri SG; Ragan JA; Ripin DHB Large-scale oxidations in the pharmaceutical industry. Chem. Rev 2006, 106, 2943–2989. - PubMed
-
- McCann SD; Stahl SS Copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidations of organic molecules: pathways for two-electron oxidation with a four-electron oxidant and a one-electron redox-active catalyst. Acc. Chem. Res 2015, 48, 1756–1766. - PubMed
-
- Liang YJ; Wei JL; Qiu X; Jiao N Homogeneous oxygenase catalysis. Chem. Rev 2018, 118, 4912–4945. - PubMed
-
- Wendlandt AE; Suess AM; Stahl SS Copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative C–H functionalizations: trends and mechanistic insights. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2011, 50, 11062–11087. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
