Protein-Based Nanohydrogels for Bioactive Delivery
- PMID: 34307293
- PMCID: PMC8299995
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.573748
Protein-Based Nanohydrogels for Bioactive Delivery
Abstract
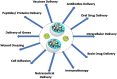
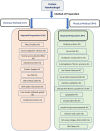
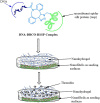
Hydrogels possess a unique three-dimensional, cross-linked network of polymers capable of absorbing large amounts of water and biological fluids without dissolving. Nanohydrogels (NGs) or nanogels are composed of diverse types of polymers of synthetic or natural origin. Their combination is bound by a chemical covalent bond or is physically cross-linked with non-covalent bonds like electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and hydrogen bonding. Its remarkable ability to absorb water or other fluids is mainly attributed to hydrophilic groups like hydroxyl, amide, and sulphate, etc. Natural biomolecules such as protein- or peptide-based nanohydrogels are an important category of hydrogels which possess high biocompatibility and metabolic degradability. The preparation of protein nanohydrogels and the subsequent encapsulation process generally involve use of environment friendly solvents and can be fabricated using different proteins, such as fibroins, albumin, collagen, elastin, gelatin, and lipoprotein, etc. involving emulsion, electrospray, and desolvation methods to name a few. Nanohydrogels are excellent biomaterials with broad applications in the areas of regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and drug delivery due to certain advantages like biodegradability, biocompatibility, tunable mechanical strength, molecular binding abilities, and customizable responses to certain stimuli like ionic concentration, pH, and temperature. The present review aims to provide an insightful analysis of protein/peptide nanohydrogels including their preparation, biophysiochemical aspects, and applications in diverse disciplines like in drug delivery, immunotherapy, intracellular delivery, nutraceutical delivery, cell adhesion, and wound dressing. Naturally occurring structural proteins that are being explored in protein nanohydrogels, along with their unique properties, are also discussed briefly. Further, the review also covers the advantages, limitations, overview of clinical potential, toxicity aspects, stability issues, and future perspectives of protein nanohydrogels.
Keywords: biodegradability; drug delivery; nanohydrogels; natural protein; polymeric networks; self-assembly.
Copyright © 2021 Chander, Kulkarni, Dhiman and Kharkwal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abaee A., Mohammadian M., Jafari S. M. (2017). Whey and Soy Protein-Based Hydrogels and Nano-Hydrogels as Bioactive Delivery Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 70, 69–81. 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.10.011 - DOI
-
- Ahmad Z., Shah A., Siddiq M., Kraatz H.-B. (2014). Polymeric Micelles as Drug Delivery Vehicles. RSC Adv. 4, 17028–17038. 10.1039/c3ra47370h - DOI
-
- Almeida H., Domingues R. M. A., Mithieux S. M., Pires R. A., Gonçalves A. I., Gómez-Florit M., et al. (2019). Tropoelastin-Coated Tendon Biomimetic Scaffolds Promote Stem Cell Tenogenic Commitment and Deposition of Elastin-Rich Matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11, 19830–19840. 10.1021/acsami.9b04616 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

