Rapid diagnosis of disseminated Mycobacterium mucogenicum infection in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimen using next-generation sequencing: A case report
- PMID: 34307617
- PMCID: PMC8281395
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i20.5621
Rapid diagnosis of disseminated Mycobacterium mucogenicum infection in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimen using next-generation sequencing: A case report
Abstract
Background: Mycobacterium mucogenicum (M. mucogenicum) belongs to the group of rapidly growing Nontuberculous mycobacteria. This microorganism is associated with a wide spectrum of infectious diseases. Due to a low detection rate or the time required for conventional culture methodology, a rapid and broad-spectrum method is necessary to identify rare pathogens.
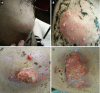
Case summary: A 12-year-old immunocompetent girl presented with painful masses for five months. The first mass was found in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, and was about 1 cm × 1.5 cm in size, tough but pliable in texture, with an irregular margin and tenderness. An abscess gradually formed and ulcerated with suppuration of the mass. Three new masses appeared on the back one by one. Chest computed tomography showed patchy and streaky cloudy opacities in both lungs. Needle aspiration of the abscess was performed, but the smear and conventional culture were negative, and the pathological examination showed no pathogens. We then performed next-generation sequencing using a formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimen to identify the pathogen. A significantly high abundance of M. mucogenicum was detected. The patient's abscesses gradually decreased in size, while inflammation in both lungs improved following 12-wk of treatment. No recurrence was observed four months after the end of the one-year treatment period.
Conclusion: Next-generation sequencing is a promising tool for the rapid and accurate diagnosis of rare pathogens, even when using a formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimen.
Keywords: Case report; Disseminated infection; Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimen; Mycobacterium mucogenicum; Next-generation sequencing; Rapid diagnosis.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium mucogenicum Infection in a Patient with an Open Fracture: A Case Report.Lab Med. 2022 Jan 6;53(1):e4-e7. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmab031. Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 34386825
-
[Study on detection of the Mycobacteria DNA in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples by triplex polymerase chain reaction].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2002 Feb;42(1):69-75. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2002. PMID: 12557351 Chinese.
-
Next-generation sequencing for hypothesis-free genomic detection of invasive tropical infections in poly-microbially contaminated, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples - a proof-of-principle assessment.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Apr 8;19(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1448-0. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30961537 Free PMC article.
-
A case of Mycobacterium mucogenicum infection in a liver transplant recipient and a review of the literature.Transpl Infect Dis. 2013 Dec;15(6):E260-3. doi: 10.1111/tid.12154. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Transpl Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24131754 Review.
-
[Mycobacterium szulgai as positive control helps to detect contaminations in the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-complex in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissues by 16SrDNA PCR].Pathologe. 2021 Feb;42(1):83-85. doi: 10.1007/s00292-021-00912-1. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Pathologe. 2021. PMID: 33475807 Review. German.
References
-
- Fleming GA, Frangoul H, Dermody TS, Halasa N. A cord blood transplant recipient with Mycobacterium mucogenicum central venous catheter infection after infusion of tap water. Pediatr Infect Dis J . 2006;25:567–569. - PubMed
-
- Decostere A, Hermans K, Haesebrouck F. Piscine mycobacteriosis: a literature review covering the agent and the disease it causes in fish and humans. Vet Microbiol . 2004;99:159–166. - PubMed
-
- El Helou G, Hachem R, Viola GM, El Zakhem A, Chaftari AM, Jiang Y, Tarrand J, Raad II. Management of rapidly growing mycobacterial bacteremia in cancer patients. Clin Infect Dis . 2013;56:843–846. - PubMed
-
- Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang Y, Jin W, Yao Y, Su Y, Huang Y, Wang M, Li B, Li H, Zhou C, Li C, Ye M, Xu X, Li Y, Hu B. Microbiological Diagnostic Performance of Metagenomic Next-generation Sequencing When Applied to Clinical Practice. Clin Infect Dis . 2018;67:S231–S240. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

