A Real-World Evidence Study of CDK4/6 Inhibitor Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Metastatic Breast Cancer by Germline BRCA Mutation Status
- PMID: 34308518
- PMCID: PMC8593114
- DOI: 10.1007/s40487-021-00162-4
A Real-World Evidence Study of CDK4/6 Inhibitor Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Metastatic Breast Cancer by Germline BRCA Mutation Status
Abstract
Introduction: Limited data exist on real-world treatment patterns and the effectiveness of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors in germline BRCA (gBRCA)-mutated breast cancer.
Methods: Adults with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (mBC) treated with CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy between 2013 and 2018 were retrospectively selected from the Flatiron Health database. Patients with known gBRCA status were classified as mutated (gBRCAm) or wild type (gBRCAwt). Time-to-first subsequent therapy or death (TFST) and overall survival (OS) were calculated from the earliest line of therapy with a CDK4/6 inhibitor.
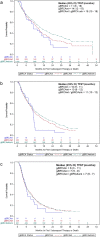
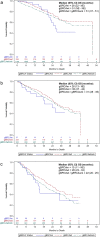
Results: Of 2968 patients with HR+/HER2- mBC receiving a CDK4/6 inhibitor, 859 (28.9%) had known gBRCA status, of whom 9.9% were gBRCAm and 90.1% gBRCAwt. Median (95% confidence interval [CI]) TFST was 10 (7-11) months in the gBRCAm group, 10 (9-11) months in the gBRCAwt group, and 11 (10-12) months in the combined gBRCAwt and unknown gBRCA group; median (95% CI) OS was 26 (21-not estimated), 37 (31-51), and 33 (31-35) months, respectively. Cox models indicated the gBRCAm group had shorter TFST (stratified hazard ratio [sHR] 1.24; 95% CI 0.96-1.59) and OS (sHR 1.50; 95% CI 1.06-2.14) than the gBRCAwt group. The gBRCAm group had shorter TFST (sHR 1.38; 95% CI 1.08-1.75) and OS (sHR 1.22; 95% CI 0.88-1.71) than the combined group.
Conclusion: The results of this real-world study suggest that treatment outcomes with CDK4/6 inhibitors may be worse in patients with gBRCAm mBC than in their counterparts with gBRCAwt and unknown gBRCA status, suggesting potential differences in tumor biology. This result highlights the unmet need in patients with gBRCAm requiring optimized treatment selection and sequencing. Future exploration in larger samples of patients who have had biomarker testing is warranted.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; Metastatic breast cancer; Survival; Treatment patterns; gBRCA mutation status.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute, Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program. Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer subtypes. 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html. Accessed 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

