[SHOX2 promotes migration, invasion and stemness of bladder cancer cells in vitro]
- PMID: 34308848
- PMCID: PMC8329670
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.07.05
[SHOX2 promotes migration, invasion and stemness of bladder cancer cells in vitro]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the role of human short stature homeobox 2 (SHOX2) in regulating the migration, invasion and stemness of human bladder cancer cells.
Methods: We analyzed SHOX2 gene expression in bladder cancer and adjacent tissues based on TCGA database. Univariate survival analysis of SHOX2 gene expression in TCGA-BLCA data was performed using GEPIA. The probable function of SHOX2 was predicted using GSEA. Human bladder cancer T24 cell models of SHOX2 knockdown or overexpression were assessed for changes in migration and invasion abilities using wound healing assay and Transwell assay, and their cancer stem cell-like characteristics were evaluated using tumorsphere formation assay and colony formation assay. Western blotting was used to detect the expressions of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers Ecadherin and vimentin and the TGF-β signaling network component TβR-I in the cells.
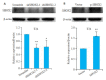
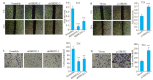
Results: SHOX2 expression was significantly higher in bladder cancer tissues than in the adjacent tissues (P < 0.05), especially in paired tissue specimens (P < 0.01), and was negatively correlated with the overall survival of the patients (P < 0.05). SHOX2 gene expression was correlated positively with EMT-related (P < 0.05) and stemness-related gene signatures (P < 0.01). In T24 cells, SHOX2 knockdown significantly suppressed cell migration and invasion, which was significantly enhanced by SHOX2 overexpression (P < 0.01). The cancer stem cell-like characteristics of T24 cells was repressed by SHOX2 knockdown but significantly enhanced by SHOX2 overexpression (P < 0.01). SHOX2 knockdown induced morphological changes of the cells into epithelioid cells, whereas SHOX2 overexpression induced a mesenchymal morphology of the cells. SHOX2 knockdown increased E-cadherin expression and decreased vimentin and TβR-I expression, while SHOX2 overexpression increased the expressions of vimentin and TβR-I in the cells.
Conclusion: SHOX2 promotes the migration, invasion and stemness of human bladder cancer cells possibly by regulating EMT via the TGF-β signaling pathway.
目的: 探讨人矮小同源盒基因2(SHOX2)对人膀胱癌细胞迁移、侵袭能力和干细胞特性的影响及其可能机制。
方法: 分析TCGA肿瘤数据库中SHOX2基因在膀胱癌标本和癌旁对照标本的表达情况,利用GEPIA网站对TCGA膀胱数据中的SHOX2基因表达量进行单因素生存分析,并利用GSEA软件预测其可能的生物学功能。选取对数生长期的人膀胱癌细胞T24,采用SHOX2 shRNA及SHOX2过表达质粒分别敲低、过表达SHOX2基因,用Western blot检测SHOX2蛋白表达量,通过划痕实验、Transwell侵袭实验检测细胞的迁移、侵袭能力,悬浮成球、克隆形成实验检测细胞的干细胞特性。在光镜下观察细胞形态变化,并用Western blot检测细胞上皮间充质转化(EMT)标志分子E-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达量的变化和TGF-β信号通路重要组件TβR-I蛋白表达量的变化。
结果: 与癌旁膀胱组织相比,SHOX2基因在TCGA膀胱癌组织中表达升高(P=0.01),在配对的膀胱癌组织中明显升高(P=0.001),SHOX2基因表达与总生存率呈负相关(P=0.01);GSEA显示SHOX2基因表达与EMT(P=0.002,P=0.03)及干细胞特性(P=0.006,P=0.008)呈正相关。在膀胱癌细胞T24中,两种不同的SHOX2 shRNA均能降低SHOX2的蛋白表达水平(shSHOX2-1,P=0.004;shSHOX2-2,P=0.03),SHOX2过表达质粒则能提高SHOX2的蛋白表达水平(P=0.007)。划痕实验、Transwell侵袭实验结果显示,抑制SHOX2表达后膀胱癌细胞的迁移(P < 0.001,P=0.02)、侵袭(P=0.002,P=0.003)能力明显降低,而SHOX2过表达则提高膀胱癌细胞的迁移(P < 0.001)、侵袭(P=0.004)能力。悬浮成球、克隆形成实验结果显示,抑制SHOX2表达后明显减弱膀胱癌细胞的干细胞特性(P=0.002,P=0.007,P < 0.001);而SHOX2过表达则增强膀胱癌细胞的干细胞特性(P=0.002,P < 0.001)。此外,抑制SHOX2表达可使细胞发生上皮样形态改变,而SHOX2过表达可使细胞发生间充质样形态改变;Western blot结果显示,抑制SHOX2表达可使膀胱癌细胞中的E-cadherin蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.001),Vimentin(P < 0.001,P=0.01)、TβR-I(P=0.03,P=0.02)蛋白表达水平降低;而SHOX2过表达可使膀胱癌细胞中的Vimentin(P=0.04)、TβR-I(P=0.003)蛋白表达水平升高。
结论: SHOX2在膀胱癌中扮演致癌基因:SHOX2增强膀胱癌细胞的迁移、侵袭能力和干细胞特性,其作用机制可能与TGF-β信号通路参与调控的EMT有关。
Keywords: EMT; SHOX2; TGF-β; bladder cancer; invasion; migration; stemness.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: a Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.] - DOI - PubMed
-
-
National Cancer Institute. Cancer of the bladder-cancer stat facts [OL]. SEER. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html.
-
-
- Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, et al. European association of urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030228382030230X. Eur Urol. 2021;79(1):82–104. [Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, et al. European association of urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(1): 82-104.] - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: AUA/SUO guideline. J Urol. 2016;196(4):1021–9. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.06.049. [Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: AUA/SUO guideline[J]. J Urol, 2016, 196(4): 1021-9.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Espinoza-Lewis RA, Chen C, et al. The role of Shox2 in SAN development and function. Pediatr Cardiol. 2012;33(6):882–9. doi: 10.1007/s00246-012-0179-x. [Liu H, Espinoza-Lewis RA, Chen C, et al. The role of Shox2 in SAN development and function[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 2012, 33(6): 882-9.] - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
