European Guidelines (S3) on diagnosis and management of mucous membrane pemphigoid, initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology - Part II
- PMID: 34309078
- PMCID: PMC8518905
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.17395
European Guidelines (S3) on diagnosis and management of mucous membrane pemphigoid, initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology - Part II
Abstract
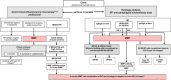
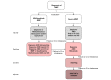
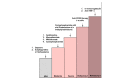
This guideline has been initiated by the task force Autoimmune Blistering Diseases of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, including physicians from all relevant disciplines and patient organizations. It is a S3 consensus-based guideline that systematically reviewed the literature on mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) in the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases until June 2019, with no limitations on language. While the first part of this guideline addressed methodology, as well as epidemiology, terminology, aetiology, clinical presentation and outcome measures in MMP, the second part presents the diagnostics and management of MMP. MMP should be suspected in cases with predominant mucosal lesions. Direct immunofluorescence microscopy to detect tissue-bound IgG, IgA and/or complement C3, combined with serological testing for circulating autoantibodies are recommended. In most patients, serum autoantibodies are present only in low levels and in variable proportions, depending on the clinical sites involved. Circulating autoantibodies are determined by indirect IF assays using tissue substrates, or ELISA using different recombinant forms of the target antigens or immunoblotting using different substrates. The major target antigen in MMP is type XVII collagen (BP180), although in 10-25% of patients laminin 332 is recognized. In 25-30% of MMP patients with anti-laminin 332 reactivity, malignancies have been associated. As first-line treatment of mild/moderate MMP, dapsone, methotrexate or tetracyclines and/or topical corticosteroids are recommended. For severe MMP, dapsone and oral or intravenous cyclophosphamide and/or oral corticosteroids are recommended as first-line regimens. Additional recommendations are given, tailored to treatment of single-site MMP such as oral, ocular, laryngeal, oesophageal and genital MMP, as well as the diagnosis of ocular MMP. Treatment recommendations are limited by the complete lack of high-quality randomized controlled trials.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
References
-
- Chan LS, Ahmed AR, Anhalt GJ et al. The first international consensus on mucous membrane pemphigoid: definition, diagnostic criteria, pathogenic factors, medical treatment, and prognostic indicators. Arch Dermatol 2002; 138: 370–379. - PubMed
-
- Chan LS. Immune‐mediated subepithelial blistering diseases of mucous membranes. Arch Dermatol 1993; 129: 448. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre M, Brette MD, Pascal F et al. A prospective study of upper aerodigestive tract manifestations of mucous membrane pemphigoid. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006; 85: 239–252. - PubMed
-
- Fine J, Neises GR, Katz SI. Immunofluorescence and immunoelecton microscopic studies in cicatricial pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol 1984; 82: 39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

