Cytologic diagnosis of metastatic melanoma by FNA: A practical review
- PMID: 34310059
- PMCID: PMC9292535
- DOI: 10.1002/cncy.22488
Cytologic diagnosis of metastatic melanoma by FNA: A practical review
Abstract
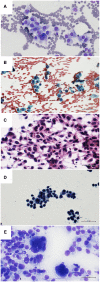
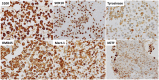
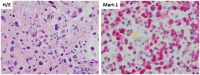
Malignant melanoma (MM) is a highly aggressive neoplasm with a growing worldwide incidence. It is not uncommon that the disease is already metastatic at the time of the first diagnosis. Regional lymph nodes and skin are the first and most common metastatic sites, followed by distant visceral sites (lungs, liver, and central nervous system) and bone. In this clinical setting, fine-needle aspiration (FNA) often represents the first diagnostic approach. FNA is a useful tool to obtain a rapid and accurate diagnosis, in conjunction with ancillary techniques and molecular analysis, as recommended by recent guidelines. The aim of this review was to describe the cytomorphology, immunocytochemical tools, and molecular tools used for the diagnosis of MM metastases on FNA.
Keywords: BRAF; fine-needle aspiration; immunocytochemistry; melanoma; sentinel node.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Cytopathology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors made no disclosures.
Figures



References
-
- Cancer Research UK . Cancer Statistics, 2011. Accessed April 30, 2021. http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

