Osteoprotegerin and RANKL-RANK-OPG-TRAIL signalling axis in heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 34313900
- PMCID: PMC9197867
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-021-10153-2
Osteoprotegerin and RANKL-RANK-OPG-TRAIL signalling axis in heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
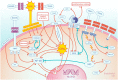
Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a glycoprotein involved in the regulation of bone remodelling. OPG regulates osteoclast activity by blocking the interaction between the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (RANK) and its ligand (RANKL). More and more studies confirm the relationship between OPG and cardiovascular diseases. Numerous studies have confirmed that a high plasma concentration of OPG and a low concentration of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) together with a high OPG/TRAIL ratio are predictors of poor prognosis in patients with myocardial infarction. A high plasma OPG concentration and a high ratio of OPG/TRAIL in the acute myocardial infarction are a prognostic indicator of adverse left ventricular remodelling and of the development of heart failure. Ever more data indicates the participation of OPG in the regulation of the function of vascular endothelial cells and the initiation of the atherosclerotic process in the arteries. Additionally, it has been shown that TRAIL has a protective effect on blood vessels and exerts an anti-atherosclerotic effect. The mechanisms of action of both OPG and TRAIL within the cells of the vascular wall are complex and remain largely unclear. However, these mechanisms of action as well as their interaction in the local vascular environment are of great interest to researchers. This article presents the current state of knowledge on the mechanisms of action of OPG and TRAIL in the circulatory system and their role in cardiovascular diseases. Understanding these mechanisms may allow their use as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases in the future.
Keywords: Endothelial cells; Heart failure; Myocardial infarction; Osteoprotegerin; RANK; TRAIL.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Korzon-Burakowska A, Burakowski S. Oś osteoprotegeryna/RANKL/RANK – rola w powikłaniach cukrzycy oraz w chorobie wieńcowej. Diabetologia Praktyczna. 2007;8(5):161–164.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

