TLR2 deficiency promotes IgE and inhibits IgG1 class-switching following ovalbumin sensitization
- PMID: 34315511
- PMCID: PMC8314519
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-021-01088-3
TLR2 deficiency promotes IgE and inhibits IgG1 class-switching following ovalbumin sensitization
Abstract
Background: To explore the roles of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 in Th2 cytokine production and immunoglobulin (Ig) class switching following ovalbumin (OVA) sensitization.
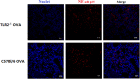
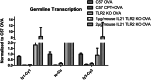
Methods: TLR2-/- and wild-type C57BL/6 mice were sensitized by intraperitoneal injection with OVA. Lung pathology was assessed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Abundance of interleukin (IL)4, IL5, IL13, and IL21 transcripts in the lungs was quantified by RT-PCR. OVA-specific IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgE and IgM were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 in lung tissue was detected by immunohistochemistry staining and nuclear factor (NF) κB activation was measured by immunofluorescence staining. STAT3 activation was inhibited using cryptotanshinone (CPT) treatment. Germline transcripts (Iμ-Cμ, Iγ-Cγ, Iα-Cα or Iε-Cε), post-recombination transcripts (Iμ-Cγ, Iμ-Cα or Iμ- Cε) and mature transcripts (VHDJH-Cγ, VHDJH-Cα or VHDJH-Cε) were analyzed from splenic B cells of OVA-sensitized wild-type mice (with or without CPT treatment) and TLR2-/- mice (with or without IL21 treatment).
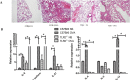
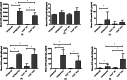
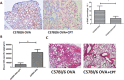
Results: The lungs of TLR2-/- mice showed a lesser degree of inflammation than wild-type mice after OVA sensitization. Following OVA sensitization, levels of IL4, IL13, and IL21, but not IL5, were significantly lower in TLR2-/- compared with wild-type mice. Moreover, OVA-specific IgG1 and IgE titers were markedly lower and higher, respectively, in TLR2-/- mice. TLR2 deficiency inhibited STAT3 activation but not NF-κB p65 activation. CPT treatment reduced IgG1 titers via inhibition of Stat3 phosphorylation. Both TLR2 knockout and CPT treatment reduced the frequencies of Iγ1-Cγ1, Iγ3-Cγ3 and Iα-Cα transcripts, but IL21 treatment compensated for the effects of TLR2 deficiency.
Conclusion: These results suggest a role of TLR2 in restricting OVA-sensitized lung inflammation via promotion of IgG1 and inhibition of IgE class switching regulated by IL21 and STAT3.
Keywords: IL21; IgE; IgG1; Ovalbumin; STAT3; Sensitization; TLR2.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Saikosaponin A ameliorates nasal inflammation by suppressing IL-6/ROR-γt/STAT3/IL-17/NF-κB pathway in OVA-induced allergic rhinitis.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jan 5;315:108874. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108874. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 31669322
-
TLR2 regulates allergic airway inflammation through NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in asthmatic mice.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(10):3138-3146. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_15073. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29863259
-
Roles of lipoxin A4 receptor activation and anti-interleukin-1β antibody on the toll-like receptor 2/mycloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB pathway in airway inflammation induced by ovalbumin.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):895-904. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3443. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25760938 Free PMC article.
-
TLR2-ERK signaling pathway regulates expression of galectin-3 in a murine model of OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation.Toxicol Lett. 2024 Jun;397:55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.05.008. Epub 2024 May 14. Toxicol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38754639
-
TLR2 favors OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation in mice through JNK signaling pathway with activation of autophagy.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117896. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117896. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32504758
Cited by
-
A biomimetic multi-component subunit vaccine via ratiometric loading of hierarchical hydrogels.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5443. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60416-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40592824 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-mediated immune imbalance in asthma: controversies, breakthroughs, and future directions.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 2;16:1605185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605185. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40672946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nieto A, Wahn U, Bufe A, Eigenmann P, Halken S, Hedlin G, Høst A, Hourihane J, Just J, Lack G, Lau S, Matricardi PM, Muraro A, Papadopoulos N, Roberts G, Simpson A, Valovirta E, Weidinger S, Wickman M, Mazon A. Allergy and asthma prevention 2014. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2014;25(6):516–533. doi: 10.1111/pai.12272. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

