Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and presymptomatic close contacts of individuals with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection: cross sectional study
- PMID: 34315770
- PMCID: PMC8314145
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.n1676
Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and presymptomatic close contacts of individuals with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection: cross sectional study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the diagnostic test accuracy of two rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and presymptomatic close contacts of people with SARS-CoV-2 infection on day 5 after exposure.
Design: Prospective cross sectional study.
Setting: Four public health service covid-19 test sites in the Netherlands.
Participants: 4274 consecutively included close contacts (identified through test-and-trace programme or contact tracing app) aged 16 years or older and asymptomatic for covid-19 when requesting a test.
Main outcome measures: Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of Veritor System (Beckton Dickinson) and Biosensor (Roche Diagnostics) rapid antigen tests, with reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing as reference standard. The viral load cut-off above which 95% of people with a positive RT-PCR test result were virus culture positive was used as a proxy of infectiousness.
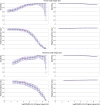
Results: Of 2678 participants tested with Veritor, 233 (8.7%) had a RT-PCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection of whom 149 were also detected by the rapid antigen test (sensitivity 63.9%, 95% confidence interval 57.4% to 70.1%). Of 1596 participants tested with Biosensor, 132 (8.3%) had a RT-PCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection of whom 83 were detected by the rapid antigen test (sensitivity 62.9%, 54.0% to 71.1%). In those who were still asymptomatic at the time of sampling, sensitivity was 58.7% (51.1% to 66.0%) for Veritor (n=2317) and 59.4% (49.2% to 69.1%) for Biosensor (n=1414), and in those who developed symptoms were 84.2% (68.7% to 94.0%; n=219) for Veritor and 73.3% (54.1% to 87.7%; n=158) for Biosensor. When a viral load cut-off was applied for infectiouness (≥5.2 log10 SARS-CoV-2 E gene copies/mL), the overall sensitivity was 90.1% (84.2% to 94.4%) for Veritor and 86.8% (78.1% to 93.0%) for Biosensor, and 88.1% (80.5% to 93.5%) for Veritor and 85.1% (74.3% to 92.6%) for Biosensor, among those who remained asymptomatic throughout. Specificities were >99%, and positive and negative predictive values were >90% and >95%, for both rapid antigen tests in all analyses.
Conclusions: The sensitivities of both rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and presymptomatic close contacts tested on day 5 onwards after close contact with an index case were more than 60%, increasing to more than 85% after a viral load cut-off was applied as a proxy for infectiousness.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf and declare: support from the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Sport for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Kucharski AJ, Klepac P, Conlan AJK, et al. CMMID COVID-19 working group . Effectiveness of isolation, testing, contact tracing, and physical distancing on reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in different settings: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis 2020;20:1151-60. 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30457-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Infectieziektebestrijding RC. COVID-19 Test-and-tracing protocol 2021 [updated 26 Feb 2021. https://lci.rivm.nl/COVID-19-bco.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
