Protective antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein vaccination are boosted in the lung after challenge in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 34315825
- PMCID: PMC9266840
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abi4547
Protective antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein vaccination are boosted in the lung after challenge in nonhuman primates
Abstract
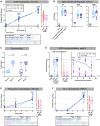
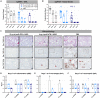
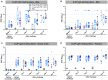
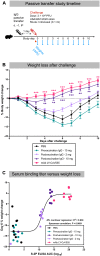
Adjuvanted soluble protein vaccines have been used extensively in humans for protection against various viral infections based on their robust induction of antibody responses. Here, soluble prefusion-stabilized spike protein trimers (preS dTM) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were formulated with the adjuvant AS03 and administered twice to nonhuman primates (NHPs). Binding and functional neutralization assays and systems serology revealed that the vaccinated NHP developed AS03-dependent multifunctional humoral responses that targeted distinct domains of the spike protein and bound to a variety of Fc receptors mediating immune cell effector functions in vitro. The neutralizing 50% inhibitory concentration titers for pseudovirus and live SARS-CoV-2 were higher than titers for a panel of human convalescent serum samples. NHPs were challenged intranasally and intratracheally with a high dose (3 × 106 plaque forming units) of SARS-CoV-2 (USA-WA1/2020 isolate). Two days after challenge, vaccinated NHPs showed rapid control of viral replication in both the upper and lower airways. Vaccinated NHPs also had increased spike protein-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody responses in the lung as early as 2 days after challenge. Moreover, passive transfer of vaccine-induced IgG to hamsters mediated protection from subsequent SARS-CoV-2 challenge. These data show that antibodies induced by the AS03-adjuvanted preS dTM vaccine were sufficient to mediate protection against SARS-CoV-2 in NHPs and that rapid anamnestic antibody responses in the lung may be a key mechanism for protection.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures


References
-
- Haynes B. F., Corey L., Fernandes P., Gilbert P. B., Hotez P. J., Rao S., Santos M. R., Schuitemaker H., Watson M., Arvin A., Prospects for a safe COVID-19 vaccine. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eabe0948 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Jackson L. A., Anderson E. J., Rouphael N. G., Roberts P. C., Makhene M., Coler R. N., McCullough M. P., Chappell J. D., Denison M. R., Stevens L. J., Pruijssers A. J., McDermott A., Flach B., Doria-Rose N. A., Corbett K. S., Morabito K. M., O’Dell S., Schmidt S. D., Swanson P. A. II, Padilla M., Mascola J. R., Neuzil K. M., Bennett H., Sun W., Peters E., Makowski M., Albert J., Cross K., Buchanan W., Pikaart-Tautges R., Ledgerwood J. E., Graham B. S., Beigel J. H.; mRNA-1273 Study Group , An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1920–1931 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Polack F. P., Thomas S. J., Kitchin N., Absalon J., Gurtman A., Lockhart S., Perez J. L., Marc G. P., Moreira E. D., Zerbini C., Bailey R., Swanson K. A., Roychoudhury S., Koury K., Li P., Kalina W. V., Cooper D., Frenck R. W. Jr., Hammitt L. L., Türeci Ö., Nell H., Schaefer A., Ünal S., Tresnan D. B., Mather S., Dormitzer P. R., Şahin U., Jansen K. U., Gruber W. C.; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group , Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S. A. C., Madhi S. A., Weckx L. Y., Folegatti P. M., Aley P. K., Angus B., Baillie V. L., Barnabas S. L., Bhorat Q. E., Bibi S., Briner C., Cicconi P., Collins A. M., Colin-Jones R., Cutland C. L., Darton T. C., Dheda K., Duncan C. J. A., Emary K. R. W., Ewer K. J., Fairlie L., Faust S. N., Feng S., Ferreira D. M., Finn A., Goodman A. L., Green C. M., Green C. A., Heath P. T., Hill C., Hill H., Hirsch I., Hodgson S. H. C., Izu A., Jackson S., Jenkin D., Joe C. C. D., Kerridge S., Koen A., Kwatra G., Lazarus R., Lawrie A. M., Lelliott A., Libri V., Lillie P. J., Mallory R., Mendes A. V. A., Milan E. P., Minassian A. M., McGregor A., Morrison H., Mujadidi Y. F., Nana A., O’Reilly P. J., Padayachee S. D., Pittella A., Plested E., Pollock K. M., Ramasamy M. N., Rhead S., Schwarzbold A. V., Singh N., Smith A., Song R., Snape M. D., Sprinz E., Sutherland R. K., Tarrant R., Thomson E. C., Török M. E., Toshner M., Turner D. P. J., Vekemans J., Villafana T. L., Watson M. E. E., Williams C. J., Douglas A. D., Hill A. V. S., Lambe T., Gilbert S. C., Pollard A. J.; Oxford COVID Vaccine Trial Group , Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 397, 99–111 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

