STING suppresses bone cancer pain via immune and neuronal modulation
- PMID: 34315904
- PMCID: PMC8316360
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24867-2
STING suppresses bone cancer pain via immune and neuronal modulation
Abstract
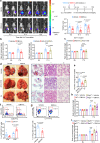
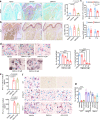
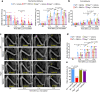
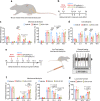
Patients with advanced stage cancers frequently suffer from severe pain as a result of bone metastasis and bone destruction, for which there is no efficacious treatment. Here, using multiple mouse models of bone cancer, we report that agonists of the immune regulator STING (stimulator of interferon genes) confer remarkable protection against cancer pain, bone destruction, and local tumor burden. Repeated systemic administration of STING agonists robustly attenuates bone cancer-induced pain and improves locomotor function. Interestingly, STING agonists produce acute pain relief through direct neuronal modulation. Additionally, STING agonists protect against local bone destruction and reduce local tumor burden through modulation of osteoclast and immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment, providing long-term cancer pain relief. Finally, these in vivo effects are dependent on host-intrinsic STING and IFN-I signaling. Overall, STING activation provides unique advantages in controlling bone cancer pain through distinct and synergistic actions on nociceptors, immune cells, and osteoclasts.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.R.J. is a consultant of Boston Scientific and received a research grant from the company. This activity is not related to this study. R.R.J. and C.R.D. filed a patent on STING-related treatment for cancer pain: “COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR THE TREATMENT OF PAIN” (PCT/US2021/028384). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

