Atrial Fibrillation Triggered by Premature Ventricular Complexes: An Under-Recognized Trigger
- PMID: 34317149
- PMCID: PMC8299860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.048
Atrial Fibrillation Triggered by Premature Ventricular Complexes: An Under-Recognized Trigger
Abstract
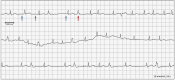
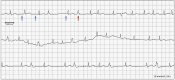
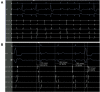
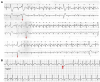
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a triggered rhythm, and ablation of the trigger is a common strategy for rhythm control. We describe a patient with symptomatic AF who was found to have episodes of AF triggered by premature ventricular complexes, likely by retrograde atrioventricular nodal conduction. (Level of Difficulty: Beginner.).
Keywords: AF, atrial fibrillation; AP, accessory pathway; PAC, premature atrial complex; PVC, premature ventricular complex; PVI, pulmonary vein isolation; ablation; atrial fibrillation; electrophysiology; palpitations.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Haissaguerre M., Jais P., Shah D.C. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:659–666. - PubMed
-
- Lin W., Tai C., Hsieh M. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation. 2003;107:3176–3183. - PubMed
-
- Santangeli P., Zado M.D., Erica S. Prevalence and distribution of focal triggers in persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:374–382. - PubMed
-
- January C., Wann L., Alpert J. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:e1–e76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

