Massive Myocardial Calcium Deposition: Hardened Heart
- PMID: 34317401
- PMCID: PMC8302108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.03.034
Massive Myocardial Calcium Deposition: Hardened Heart
Abstract
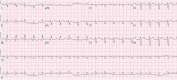
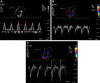
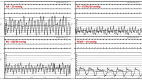
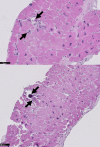
A 25-year-old African-American woman with end-stage renal disease presented with new-onset heart failure. Transthoracic echocardiography indicated a significantly hyperechoic myocardium, and computed tomography noted a circumferential hyperattenuated myocardium. Endomyocardial biopsy revealed focal interstitial and intramyocyte calcium deposition in the heart, confirming a rare diagnosis of massive myocardial calcium deposition. (Level of Difficulty: Beginner.).
Keywords: CT, computed tomographic; EMB, endomyocardial biopsy; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; HF, heart failure; cardiomyopathy; disorders of calcium metabolism; restrictive.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Na J.Y. A heart of stone: an autopsy case of massive myocardial calcification. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2018;14:102–105. - PubMed
-
- Isotalo P.A., Halil A., Green M., Tang A., Lach B., Veinot J.P. Metastatic calcification of the cardiac conduction system with heart block: an under-reported entity in chronic renal failure patients. J Forensic Sci. 2000;45:1335–1338. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

