An Unusual Complication of Transseptal Puncture
- PMID: 34317466
- PMCID: PMC8305646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.11.038
An Unusual Complication of Transseptal Puncture
Abstract
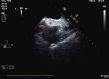
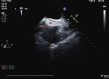
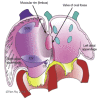
The interatrial septum is a structure with complex embryological development. The true atrial septum is a circumscribed structure, and transgression outside of this area during transseptal puncture may result in entry into the extracardiac space or aorta that may result in a pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade. (Level of Difficulty: Intermediate.).
Keywords: IAS, interatrial septum; SVC, superior vena cava; atrial fibrillation; complication; electrophysiology; pericardial effusion.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transseptal Puncture Through an Interatrial Septum With Lipomatous Hypertrophy: A False Perception of Success and Failure.Cureus. 2022 Sep 29;14(9):e29737. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29737. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36324361 Free PMC article.
-
Interatrial septum dissection and atrial wall hematoma following transseptal puncture: A systematic review of the literature.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Aug;96(2):424-431. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28554. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 31642609
-
Transseptal access for left atrial ablation: the catheter-probing techniques are not without risk.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014 May;25(5):479-484. doi: 10.1111/jce.12356. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24384060
-
Transseptal puncture and catheter ablation via the superior vena cava approach for persistent atrial fibrillation in a patient with polysplenia syndrome and interruption of the inferior vena cava: contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation.Europace. 2017 Jul 1;19(7):1227-1232. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw095. Europace. 2017. PMID: 27174901
-
Current Concepts of Anatomy, Electrophysiology, and Therapeutic Implications of the Interatrial Septum.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2019 Jun;5(6):647-656. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2019.04.013. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31221350 Review.
Cited by
-
Inadvertent left atrial injury during transseptal puncture with a radiofrequency-powered wire.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023 Oct;66(7):1561-1562. doi: 10.1007/s10840-023-01560-6. Epub 2023 May 27. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37237134 No abstract available.
-
Interatrial septum dissection and closure from transseptal puncture during mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2024 Nov 2;8(11):ytae559. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytae559. eCollection 2024 Nov. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39545161 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Tamponade After Transseptal Puncture: Focus on the Mechanism of a Rare But Life-Threatening Complication.JACC Case Rep. 2025 Apr 2;30(7):103379. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2025.103379. JACC Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40185610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- January C.T., Wann L.S., Calkins H. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:104–132. - PubMed
-
- Cournand A.M.H. Recording of blood pressure from the left auricle and the pulmonary veins in human subjects with interauricular septal defect. Am J Physiol. 1947;150:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Brockenbrough E.C., Braunwald E.R.J. Transseptal left heart catheterization. A review of 450 studies and description of an improved technic. Circulation. 1962;25:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Katritsis G.D., Siontis G.C.M., Giazitzoglou E., Fragakis N., Katritsis D.G. Complications of transseptal catheterization for different cardiac procedures. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:5352–5354. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R.B.N. The anatomy of the heart revisited. Anat Rec. 1996;246:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

