Bicuspid aortic valve repair using geometric ring annuloplasty: A first-in-humans pilot trial
- PMID: 34317698
- PMCID: PMC8288553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2019.12.005
Bicuspid aortic valve repair using geometric ring annuloplasty: A first-in-humans pilot trial
Abstract
Objective: As bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) repair evolves, more effective annular reduction and stabilization could be advantageous. A geometric annuloplasty ring has been developed, and 2-year regulatory outcomes of a first-in-humans pilot trial are reported.
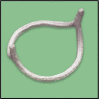
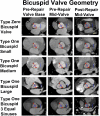
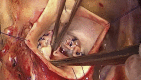
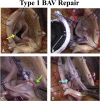
Methods: A prospective first-in-humans trial of BAV ring annuloplasty was completed in 16 patients. Patient age was 44.4 ± 11.3 (mean ± standard deviation) years, preoperative aortic insufficiency grade was 2.5 ± 1.0, New York Heart Association class 1.8 ± 0.4, and mean systolic gradient 13.4 ± 12.9 mm Hg. Three patients had Sievers type 0 BAV, 11 had type 1, and 2 were type 2. The Dacron-covered titanium rings had circular base geometry with 180° subcommissural posts and were implanted subannularly. Leaflets were reconstructed using plication/cleft closure, creating an effective height of ≥8 mm, even if modest gradients were induced.
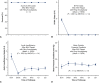
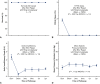
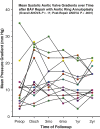
Results: Mean pre-repair annular diameter was 28.6 ± 3.3 mm, and the average ring diameter was 22.3 ± 1.6 mm. All valves required leaflet plication/reconstruction; pericardium was avoided; and 7 patients had aortic replacement for aneurysms. No early mortalities or major complications occurred. Two patients required early prosthetic valve replacement for technical errors, and all were between 24-38 months' postoperative at follow-up. No late mortalities or valve-related complications occurred, and all patients reverted to New York Heart Association class I. Aortic insufficiency reduction was significant to grade 0.9 ± 0.5 at 2-years (P < .0001). Mean valve gradients were acceptable (13.3 ± 5.0 mm Hg at 2 years; overall P = .11) and tended to fall over time (P < .0001).
Conclusions: Geometric ring annuloplasty was safe and effective for BAV repair. AI reduction was significant, valve gradients were satisfactory, and clinical outcomes were excellent. Geometric ring annuloplasty could simplify and standardize BAV repair.
Keywords: AI, aortic insufficiency; AVR, aortic valve replacement; BAV, bicuspid aortic valve; aortic annuloplasty; aortic valve repair; bicuspid aortic valve.
© 2020 by The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aicher D., Fries R., Rodionycheva S., Schmidt K., Langer F., Schafers H.J. Aortic valve repair leads to a low incidence of valve-related complications. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37:127–132. - PubMed
-
- Price J., De Kerchove L., Glineur D., Vanoverschelde J.L., Noirhomme P., El Khoury G. Risk of valve-related events after aortic valve repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:606–612. discussion 13. - PubMed
-
- de Meester C., Pasquet A., Gerber B.L., Vancraeynest D., Noirhomme P., El Khoury G., et al. Valve repair improves the outcome of surgery for chronic severe aortic regurgitation: a propensity score analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:1913–1920. - PubMed
-
- Yang B., Patel H.J., Sorek C., Hornsby W.E., Wu X., Ward S., et al. Sixtenn-year experience of David and Bentall procedures in acute type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105:779–784. - PubMed
-
- Svensson L.G., Batizy L.H., Blackstone E.H., Gillinov A.M., Moon M.C., D'Agostino R.S., et al. Results of matching valve and root repair to aortic valve and root pathology. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:1491–1498.e7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

