A blood-based prognostic liver secretome signature and long-term hepatocellular carcinoma risk in advanced liver fibrosis
- PMID: 34318286
- PMCID: PMC8312635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.03.017
A blood-based prognostic liver secretome signature and long-term hepatocellular carcinoma risk in advanced liver fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Accurate non-invasive prediction of long-term hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) risk in advanced liver fibrosis is urgently needed for cost-effective HCC screening; however, this currently remains an unmet need.
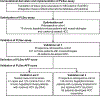
Methods: A serum-protein-based prognostic liver secretome signature (PLSec) was bioinformatically derived from previously validated hepatic transcriptome signatures and optimized in 79 patients with advanced liver fibrosis. We independently validated PLSec for HCC risk in 331 cirrhosis patients with mixed etiologies (validation set 1 [V1]) and thereafter developed a score with clinical prognostic variables. The score was then validated in two independent cohorts: validation set 2 (V2): 164 patients with advanced liver fibrosis due to hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection cured after direct-acting antiviral therapy; validation set 3 (V3): 146 patients with advanced liver fibrosis with successfully-treated HCC and cured HCV infection.
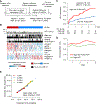
Findings: An 8-protein blood-based PLSec recapitulated transcriptome-based hepatic HCC risk status. In V1, PLSec was significantly associated with incident HCC risk (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.35; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.30-4.23). A composite score with serum alpha-fetoprotein (PLSec-AFP) was defined in V1, and validated in V2 (adjusted odds ratio, 3.80 [95%CI, 1.66-8.66]) and V3 (aHR, 3.08 [95%CI, 1.78-5.31]; c-index, 0.74). PLSec-AFP outperformed AFP alone (Brier score, 0.165 vs. 0.186 in V2; 0.196 vs. 0.206 in V3, respectively).
Conclusions: The blood-based PLSec-AFP can accurately stratify patients with advanced liver fibrosis for long-term HCC risk and thereby guide risk-based tailored HCC screening.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS Y.H. serves as an advisory board member for Helio Health and founding shareholder for Alentis Therapeutics, and received a research funding from Morphic Therapeutics. T.F.B. serves as advisor and is a founding shareholder or Alentis Therapeutics. R.T received a lecture fee from Bayer, Chugai, Eisai, Takeda and Wako/Fujifilm. N.P. has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers-Squibb, Exact Sciences, Eli Lilly, and Freenome. A.G.S. has served on advisory boards of Genentech, Eisai, Bayer, Exelixis, Wako/Fujifilm and has received research funding from Bayer, Target Pharmasolutions, Exact Sciences, and Glycotest.
Figures


Comment in
-
PLSec: A novel, liquid biomarker for HCC risk.Med. 2021 Jul 9;2(7):788-790. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.06.004. Med. 2021. PMID: 35590215
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, et al.Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018;68:723–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
