Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications
- PMID: 34319011
- PMCID: PMC8456215
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202100275
Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications
Abstract
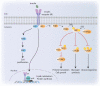
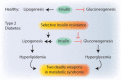
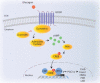
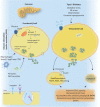
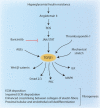
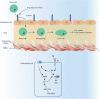
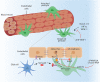
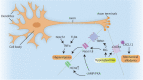
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic, chronic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels. Although a large drug portfolio exists to keep the blood glucose levels under control, these medications are not without side effects. More importantly, once diagnosed diabetes is rarely reversible. Dysfunctions in the kidney, retina, cardiovascular system, neurons, and liver represent the common complications of diabetes, which again lack effective therapies that can reverse organ injury. Overall, the molecular mechanisms of how type 2 diabetes develops and leads to irreparable organ damage remain elusive. This review particularly focuses on novel targets that may play role in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Further research on these targets may eventually pave the way to novel therapies for the treatment-or even the prevention-of type 2 diabetes along with its complications.
Keywords: insulin resistance; metabolism; signaling pathways; type 2 diabetes, diabetic complications.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Introduction to diabetes mellitus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;771:1-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5441-0_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23393665 Review.
-
Type 2 diabetes: where we are today: an overview of disease burden, current treatments, and treatment strategies.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009 Sep-Oct;49 Suppl 1:S3-9. doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2009.09077. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009. PMID: 19801365 Review.
-
Multiple drug targets in the management of type 2 diabetes.Curr Drug Targets. 2002 Jun;3(3):203-21. doi: 10.2174/1389450023347803. Curr Drug Targets. 2002. PMID: 12041735 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 90-year perspective.Postgrad Med J. 2016 Feb;92(1084):63-9. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2015-133281. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Postgrad Med J. 2016. PMID: 26621825 Review.
-
TRPV1: A novel target for the therapy of diabetes and diabetic complications.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;984:177021. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177021. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39362389 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal Nogo-B reduces GLP1 levels by binding to proglucagon on the endoplasmic reticulum to inhibit PCSK1 cleavage.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 10;15(1):6845. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51352-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39122737 Free PMC article.
-
New discoveries in the field of metabolism by applying single-cell and spatial omics.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Jul;13(7):711-725. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 4. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 37577385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of the Case Reports on Metformin, Sulfonylurea, and Thiazolidinedione Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Med Sci (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;11(3):50. doi: 10.3390/medsci11030050. Med Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37606429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinase C (PKC)-mediated TGF-β Regulation in Diabetic Neuropathy: Emphasis on Neuro-inflammation and Allodynia.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(7):777-788. doi: 10.2174/0118715303262824231024104849. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37937564 Review.
-
Comparative diabetes mellitus burden trends across global, Chinese, US, and Indian populations using GBD 2021 database.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 8;15(1):11955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96175-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40200037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banting F. G., Best C. H., Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 251. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y., Ley S. H., Hu F. B., Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88. - PubMed
-
- Ahlqvist E., Storm P., Käräjämäki A., Martinell M., Dorkhan M., Carlsson A., Vikman P., Prasad R. B., Aly D. M., Almgren P., Wessman Y., Shaat N., Spégel P., Mulder H., Lindholm E., Melander O., Hansson O., Malmqvist U., Lernmark Å., Lahti K., Forsén T., Tuomi T., Rosengren A. H., Groop L., Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
