Early Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) by miR-138 and miR-424-5p Expression as a Cancer Marker
- PMID: 34319042
- PMCID: PMC8607090
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.7.2185
Early Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) by miR-138 and miR-424-5p Expression as a Cancer Marker
Abstract
Introduction: MicroRNAs (miRs) are a group of endogenous, non-coding, 18-24 nucleotide length single-strand RNAs. These molecules mediate the gene expression and are involved in regulating diverse cellular biological processes, i.e. cell cycle, differentiation, and apoptosis. Aberrant miR expression has been shown to be an important event in the pathologies of various types of cancer, including oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods: Blood samples were obtained from 30 patients (15 cases and 15 controls), to determine miR-138 and miR-424-5p expression by using real-time PCR and ΔΔCT.
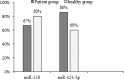
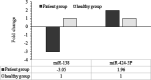
Results: The median CT values of miR-138 were 27.60 and 28.70, while those of miR 424-5p were 29.40 and 30.0 in the case and control groups, respectively. Mann-Whitney test indicated no significant difference in miR-138 and miR-424-5p between the two groups (P > 0.05). However, results obtained by ΔΔCT method showed that miR-424-5p expression was 1.96 times higher in the case group, but miR-138 expression was 3.05 times lower in the plasma of OSCC patients.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the evaluation of miR-138 and miR-424-5p expression in serum can be used as potent markers for carcinoma detection and also may be a potentially therapeutic approach in the future. Further longitudinal studies with larger samples are required to verify these findings.<br />.
Keywords: miR 138; miR 424-5p; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Expression Levels of miR-21-5p and miR-429 Genes in Biopsy Samples from Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 25;13(7):1244. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071244. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046462 Free PMC article.
-
Serum miR-483-5p: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):447-53. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3514-z. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26224475
-
MiRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers in the serum of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorder (OPMD) patients.Arch Oral Biol. 2023 Mar;147:105627. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2023.105627. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Arch Oral Biol. 2023. PMID: 36657275
-
Role of miR153 and miR455-5p Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Isolated from Plasma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jan 1;22(1):157-161. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.1.157. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33507694 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-590-5p regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RECK.Histol Histopathol. 2021 Mar;36(3):355-365. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-306. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Histol Histopathol. 2021. PMID: 33447989
Cited by
-
Role of miR-424 in the carcinogenesis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Jan;26(1):16-38. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03209-2. Epub 2023 May 13. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37178445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 26;23(15):8257. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158257. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Biomarkers for Screening.J Dent (Shiraz). 2024 Mar 1;25(1):1-16. doi: 10.30476/dentjods.2023.96159.1924. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Dent (Shiraz). 2024. PMID: 38544776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dauriporphine inhibited lung cancer cell viability, motility, and energy metabolism through the miR-424-5p/MAPK14 axis.Hereditas. 2025 Jun 11;162(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00473-w. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40500789 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (miR-24, miR-200, and miR-34): Screening and Detection MicroRNA.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jul 1;25(7):2265-2269. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.7.2265. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39068557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1143–54. - PubMed