Enantioselective α-Chlorination Reactions of in Situ Generated C1 Ammonium Enolates under Base-Free Conditions
- PMID: 34319102
- PMCID: PMC8353620
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c02256
Enantioselective α-Chlorination Reactions of in Situ Generated C1 Ammonium Enolates under Base-Free Conditions
Abstract
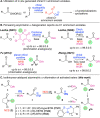
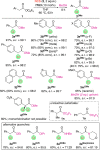
The asymmetric α-chlorination of activated aryl acetic acid esters can be carried out with high levels of enantioselectivities utilizing commercially available isothiourea catalysts under base-free conditions. The reaction, which proceeds via the in situ formation of chiral C1 ammonium enolates, is best carried out under cryogenic conditions combined with a direct trapping of the activated α-chlorinated ester derivative to prevent epimerization, thus allowing for enantioselectivities of up to e.r. 99:1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Photochemical Wolff Rearrangement Initiated Generation and Subsequent α-Chlorination of C1 Ammonium Enolates.Org Lett. 2023 May 5;25(17):3126-3130. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00986. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Org Lett. 2023. PMID: 37098273 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective isothiourea-catalysed α-fluorination of C1-ammonium enolates generated from arylesters.J Fluor Chem. 2025 Apr;283-284:110434. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2025.110434. J Fluor Chem. 2025. PMID: 40620791 Free PMC article.
-
Isothiourea and Brønsted Acid Cooperative Catalysis: Enantioselective Construction of Dihydropyridinones.Org Lett. 2020 Mar 20;22(6):2261-2265. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00461. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Org Lett. 2020. PMID: 32119556
-
Generation and Reactivity of C(1)-Ammonium Enolates by Using Isothiourea Catalysis.Chemistry. 2021 Jan 21;27(5):1533-1555. doi: 10.1002/chem.202002059. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 32557875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acid-base catalysis of chiral Pd complexes: development of novel catalytic asymmetric reactions and their application to synthesis of drug candidates.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2006 Oct;54(10):1351-64. doi: 10.1248/cpb.54.1351. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2006. PMID: 17015970 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of α-Chloroarylacetic Acid via Electrochemical Carboxylation of α,α-Dichloroarylmethane Derivatives.Molecules. 2023 Sep 20;28(18):6704. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186704. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764480 Free PMC article.
-
Photochemical Wolff Rearrangement Initiated Generation and Subsequent α-Chlorination of C1 Ammonium Enolates.Org Lett. 2023 May 5;25(17):3126-3130. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00986. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Org Lett. 2023. PMID: 37098273 Free PMC article.
-
Lactone Enolates of Isochroman-3-ones and 2-Coumaranones: Quantification of Their Nucleophilicity in DMSO and Conjugate Additions to Chalcones.J Org Chem. 2024 May 17;89(10):6915-6928. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c00277. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Org Chem. 2024. PMID: 38687827 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective isothiourea-catalysed α-fluorination of C1-ammonium enolates generated from arylesters.J Fluor Chem. 2025 Apr;283-284:110434. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2025.110434. J Fluor Chem. 2025. PMID: 40620791 Free PMC article.
-
Isothiourea-Catalyzed Enantioselective Functionalisation of Glycine Schiff Base Aryl Esters via 1,6- and 1,4-Additions.ChemistryEurope. 2023 Jul 3;1(1):e202300015. doi: 10.1002/ceur.202300015. Epub 2023 May 3. ChemistryEurope. 2023. PMID: 38882579 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
For selected overviews of the asymmetric α-heterofunctionalization reactions using different catalysis concepts, see:
- Oestreich M. Strategies for Catalytic Asymmetric Electrophilic α Halogenation of Carbonyl Compounds. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2324–2327. 10.1002/anie.200500478. - DOI - PubMed
- France S.; Weatherwax A.; Lectka T. Recent Developments in Catalytic, Asymmetric α-Halogenation: A New Frontier in Asymmetric Catalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 475–479. 10.1002/ejoc.200400517. - DOI
- Guillena G.; Ramón D. J. Enantioselective α-heterofunctionalisation of carbonyl compounds: organocatalysis is the simplest approach. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2006, 17, 1465–1492. 10.1016/j.tetasy.2006.05.020. - DOI
- Ueda M.; Kano T.; Maruoka K. Organocatalyzed direct asymmetric α-halogenation of carbonyl compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2005–2012. 10.1039/b901449g. - DOI - PubMed
- Smith A. M. R.; Hii K. K. Transition Metal Catalyzed Enantioselective α-Heterofunctionalization of Carbonyl Compounds. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1637–1656. 10.1021/cr100197z. - DOI - PubMed
- Russo A.; De Fusco C.; Lattanzi A. Enantioselective organocatalytic α-heterofunctionalization of active methines. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 385–397. 10.1039/C1RA00612F. - DOI
- Schörgenhumer J.; Tiffner M.; Waser M. Chiral Phase-Transfer Catalysis in the Asymmetric α-Heterofunctionalization of Prochiral Nucleophiles. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1753–1769. 10.3762/bjoc.13.170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
-
-
For a recent overview, see:
- Eder I.; Haider V.; Zebrowski P.; Waser M. Recent Progress in the Asymmetric Syntheses of α-Heterofunctionalized (Masked) α- and β-Amino Acid Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 202–219. 10.1002/ejoc.202001077. - DOI
-
-
-
For an illustrative overview, see:
- Freckleton M.; Baeza A.; Benavent L.; Chinchilla R. Asymmetric Organocatalytic Electrophilic Heterofunctionalization of Oxindoles. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1006–1014. 10.1002/ajoc.201800146. - DOI
-
-
- Fu G. C. Asymmetric Catalysis with “Planar-Chiral” Derivatives of 4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 542–547. 10.1021/ar030051b. - DOI - PubMed
- Gaunt M. J.; Johansson C. C. C. Recent Developments in the Use of Catalytic Asymmetric Ammonium Enolates in Chemical Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5596–5605. 10.1021/cr0683764. - DOI - PubMed
- Morrill L. C.; Smith A. D. Organocatalytic Lewis base functionalization of carboxylic acids, esters and anhydrides via C1-ammonium or azolium enolates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6214–6226. 10.1039/C4CS00042K. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

