Staphylococcal TSST-1 Association with Eczema Herpeticum in Humans
- PMID: 34319127
- PMCID: PMC8386428
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00608-21
Staphylococcal TSST-1 Association with Eczema Herpeticum in Humans
Abstract
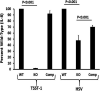
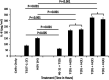
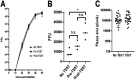
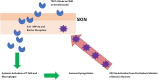
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a condition affecting 30 million persons in the United States. AD patients are heavily infected with Staphylococcus aureus on the skin. A particularly severe form of AD is eczema herpeticum (ADEH), where the patients' AD is complicated by S. aureus and herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. This study examined the S. aureus strains from 15 ADEH patients, provided blinded, and showed a high association of ADEH with strains that produce toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1; 73%) compared to 10% production by typical AD isolates from patients without EH and those from another unrelated condition, cystic fibrosis. The ADEH isolates produced the superantigens associated with TSS (TSST-1 and staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, and C). This association may in part explain the potential severity of ADEH. We also examined the effect of TSST-1 and HSV-1 on human epithelial cells and keratinocytes. TSST-1 used CD40 as its receptor on epithelial cells, and HSV-1 either directly or indirectly interacted with CD40. The consequence of these interactions was chemokine production, which is capable of causing harmful inflammation, with epidermal/keratinocyte barrier disruption. Human epithelial cells treated first with TSST-1 and then HSV-1 resulted in enhanced chemokine production. Finally, we showed that TSST-1 modestly increased HSV-1 replication but did not increase viral plaque size. Our data suggest that ADEH is associated with production of the major TSS-associated superantigens, together with HSV reactivation. The superantigens plus HSV may damage the skin barrier by causing harmful inflammation, thereby leading to increased symptoms. IMPORTANCE Atopic dermatitis (eczema, AD) with concurrent herpes simplex virus infection (eczema herpeticum, ADEH) is a severe form of AD. We show that ADEH patients are colonized with Staphylococcus aureus that primarily produces the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1); however, significantly but to a lesser extent the superantigens staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, and C are also represented in ADEH. Our studies showed that TSST-1 uses the immune costimulatory molecule CD40 as its epithelial cell receptor. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) also interacted directly or indirectly with CD40 on epithelial cells. Treatment of epithelial cells with TSST-1 and then HSV-1 resulted in enhanced chemokine production. We propose that this combination of exposures (TSST-1 and then HSV) leads to opening of epithelial and skin barriers to facilitate potentially serious ADEH.
Keywords: CD40; Staphylococcus aureus; atopic dermatitis; chemokines; eczema; eczema herpeticum; epithelial cells; herpes simplex virus; staphylococcal enterotoxins; toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal Superantigens Stimulate Epithelial Cells through CD40 To Produce Chemokines.mBio. 2019 Mar 19;10(2):e00214-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00214-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30890614 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of antibody to toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 in burn patients.Ann Lab Med. 2015 Jan;35(1):89-93. doi: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.89. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Ann Lab Med. 2015. PMID: 25553286 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 Evaluation and Antibiotic Impact in a Transgenic Model of Staphylococcal Soft Tissue Infection.mSphere. 2019 Oct 9;4(5):e00665-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00665-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31597722 Free PMC article.
-
Eczema herpeticum in atopic dermatitis.Allergy. 2021 Oct;76(10):3017-3027. doi: 10.1111/all.14853. Epub 2021 May 3. Allergy. 2021. PMID: 33844308 Review.
-
Immune response to staphylococcal superantigens.Immunol Res. 1999;20(2):163-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02786471. Immunol Res. 1999. PMID: 10580640 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B and C Mutants and Vaccine Toxoids.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 23;11(2):e0444622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04446-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36815779 Free PMC article.
-
History of S. aureus Skin Infection Significantly Associates with History of Eczema Herpeticum in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Oct;13(10):2417-2429. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-00996-y. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37615834 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid reduction in Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis subjects following dupilumab treatment.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Nov;152(5):1179-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.05.026. Epub 2023 Jun 13. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37315812 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) in Staphylococcus aureus: Prevalence, Molecular Mechanisms, and Public Health Implications.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;17(7):323. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070323. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S. aureus virulence factors decrease epithelial barrier function and increase susceptibility to viral infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 22;11(5):e0168423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01684-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37737609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leung DY, Gao PS, Grigoryev DN, Rafaels NM, Streib JE, Howell MD, Taylor PA, Boguniewicz M, Canniff J, Armstrong B, Zaccaro DJ, Schneider LC, Hata TR, Hanifin JM, Beck LA, Weinberg A, Barnes KC. 2011. Human atopic dermatitis complicated by eczema herpeticum is associated with abnormalities in IFN-gamma response. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:965–973.e1-5. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck LA, Boguniewicz M, Hata T, Schneider LC, Hanifin J, Gallo R, Paller AS, Lieff S, Reese J, Zaccaro D, Milgrom H, Barnes KC, Leung DY. 2009. Phenotype of atopic dermatitis subjects with a history of eczema herpeticum. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:260–269.E7. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merriman JA, Mueller EA, Cahill MP, Beck LA, Paller AS, Hanifin JM, Ong PY, Schneider L, Babineau DC, David G, Lockhart A, Artis K, Leung DY, Schlievert PM. 2016. Temporal and racial differences associated with atopic dermatitis Staphylococcus aureus and encoded virulence factors. mSphere 1:e00295-16. doi:10.1128/mSphere.00295-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

