MicroRNA-486 promotes a more catabolic phenotype in chondrocyte-like cells by targeting SIRT6 : possible involvement in cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis
- PMID: 34319136
- PMCID: PMC8333035
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.107.BJR-2019-0251.R4
MicroRNA-486 promotes a more catabolic phenotype in chondrocyte-like cells by targeting SIRT6 : possible involvement in cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis
Abstract
Aims: Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by persistent destruction of articular cartilage. It has been found that microRNAs (miRNAs) are closely related to the occurrence and development of OA. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the mechanism of miR-486 in the development and progression of OA.
Methods: The expression levels of miR-486 in cartilage were determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The expression of collagen, type II, alpha 1 (COL2A1), aggrecan (ACAN), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13, and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4 (ADAMTS4) in SW1353 cells at both messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels was determined by qRT-PCR, western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Double luciferase reporter gene assay, qRT-PCR, and western blot assay were used to determine whether silencing information regulator 6 (SIRT6) was involved in miR-486 induction of chondrocyte-like cells to a more catabolic phenotype.
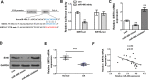
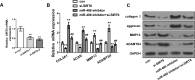
Results: Compared with osteonecrosis, the expression of miR-486 was significantly upregulated in cartilage from subjects with severe OA. In addition, overexpressed miR-486 promoted a catabolic phenotype in SW1353 cells by upregulating the expressions of ADAMTS4 and MMP-13 and down-regulating the expressions of COL2A1 and ACAN. Conversely, inhibition of miR-486 had the opposite effect. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-486 significantly inhibited the expression of SIRT6, confirming that SIRT6 is a direct target of miR-486. Moreover, SW1353 cells were transfected with small interfering RNA (si)-SIRT6 and it was found that SIRT6 was involved in and inhibited miR-486-induced changes to SW1353 gene expression.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that miR-486 promotes a catabolic phenotype in SW1353 cells in OA by targeting SIRT6. Our findings might provide a potential therapeutic target and theoretical basis for OA. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2021;10(7):459-466.
Keywords: Chondrocyte catabolic phenotype; Osteoarthritis; SIRT6; SW1353 cell line; miR-486.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Silencing of microRNA-138-5p promotes IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes by targeting FOXC1: miR-138 promotes cartilage degradation.Bone Joint Res. 2016 Oct;5(10):523-530. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.510.BJR-2016-0074.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2016. PMID: 27799147 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA circ-IQGAP1 Knockdown Alleviates Interleukin-1β-Induced Osteoarthritis Progression via Targeting miR-671-5p/TCF4.Orthop Surg. 2021 May;13(3):1036-1046. doi: 10.1111/os.12923. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33675175 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0001103 alleviates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte cell injuries by upregulating SIRT1 via targeting miR-375.Clin Immunol. 2021 Jun;227:108718. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108718. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33819576
-
LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-145 Adjusts IL-1β-Induced Chondrocytes Viability and Cartilage Matrix Degradation by Regulating ADAMTS5 in Human Osteoarthritis.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Nov;60(11):1081-1092. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1081. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 31637891 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-33b-3p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation by targeting DNMT3A in osteoarthritis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Nov 5;519(2):430-437. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.022. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31522815
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory role of T helper cells in rheumatoid arthritis : a comprehensive research review.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Jul;11(7):426-438. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.117.BJR-2021-0594.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 35775145 Free PMC article.
-
Suramin enhances chondrogenic properties by regulating the p67phox/PI3K/AKT/SOX9 signalling pathway.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):723-738. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1110.BJR-2022-0013.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 36222195 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analyses and machine-learning methods reveal dysregulated key genes and potential pathogenesis in human osteoarthritic cartilage.Bone Joint Res. 2024 Feb 5;13(2):66-82. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.132.BJR-2023-0074.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2024. PMID: 38310924 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-98-5p plays suppressive effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury associated with osteoarthritis by targeting CASP3.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 13;19(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04628-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38615043 Free PMC article.
-
Cartilage-specific Sirt6 deficiency represses IGF-1 and enhances osteoarthritis severity in mice.Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Nov;82(11):1464-1473. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224385. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37550003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guyot P, Pandhi S, Nixon RM, Iqbal A, Chaves RL, Andrew Moore R. Efficacy and safety of diclofenac in osteoarthritis: results of a network meta-analysis of unpublished legacy studies. Scand J Pain. 2017;16(Suppl 2):74–88. - PubMed
-
- Breivik H. NSAIDs relieve osteoarthritis (OA) pain, but cardiovascular safety in question even for diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib: what are the alternatives? Scand J Pain. 2017;16:148–149. - PubMed

