Prion Dissemination through the Environment and Medical Practices: Facts and Risks for Human Health
- PMID: 34319151
- PMCID: PMC8404694
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00059-19
Prion Dissemination through the Environment and Medical Practices: Facts and Risks for Human Health
Abstract
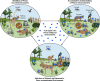
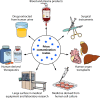
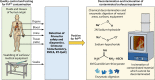
Prion diseases are a group of fatal, infectious neurodegenerative disorders affecting various species of mammals, including humans. The infectious agent in these diseases, termed prion, is composed exclusively of a misfolded protein that can spread and multiply in the absence of genetic materials. In this article, we provide an overview of the mechanisms of prion replication, interindividual transmission, and dissemination in communities. In particular, we review the potential role of the natural environment in prion transmission, including the mechanisms and pathways for prion entry and accumulation in the environment as well as its roles in prion mutation, adaptation, evolution, and transmission. We also discuss the transmission of prion diseases through medical practices, scientific research, and use of biological products. Detailed knowledge of these aspects is crucial to limit the spreading of existing prion diseases as well as to prevent the emergence of new diseases with possible catastrophic consequences for public health.
Figures

References
-
- Creutzfeldt HG. 1920. Über eine eigenartige herdförmige Erkrankung des Zentralnervensystems (Vorläufige mitteilung). Z Gesamte Neurol Psy 57:1–18. 10.1007/BF02866081. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

