Genome-Wide Patterns of Bracovirus Chromosomal Integration into Multiple Host Tissues during Parasitism
- PMID: 34319152
- PMCID: PMC8549517
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00684-21
Genome-Wide Patterns of Bracovirus Chromosomal Integration into Multiple Host Tissues during Parasitism
Abstract
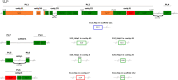
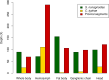
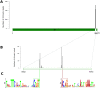
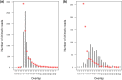
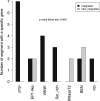
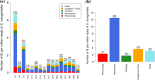
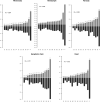
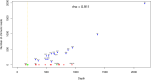
Bracoviruses are domesticated viruses found in parasitic wasp genomes. They are composed of genes of nudiviral origin that are involved in particle production and proviral segments containing virulence genes that are necessary for parasitism success. During particle production, proviral segments are amplified and individually packaged as DNA circles in nucleocapsids. These particles are injected by parasitic wasps into host larvae together with their eggs. Bracovirus circles of two wasp species were reported to undergo chromosomal integration in parasitized host hemocytes, through a conserved sequence named the host integration motif (HIM). Here, we used bulk Illumina sequencing to survey integrations of Cotesia typhae bracovirus circles in the DNA of its host, the maize corn borer (Sesamia nonagrioides), 7 days after parasitism. First, assembly and annotation of a high-quality genome for C. typhae enabled us to characterize 27 proviral segments clustered in proviral loci. Using these data, we characterized large numbers of chromosomal integrations (from 12 to 85 events per host haploid genome) for all 16 bracovirus circles containing a HIM. Integrations were found in four S. nonagrioides tissues and in the body of a caterpillar in which parasitism had failed. The 12 remaining circles do not integrate but are maintained at high levels in host tissues. Surprisingly, we found that HIM-mediated chromosomal integration in the wasp germ line has occurred accidentally at least six times during evolution. Overall, our study furthers our understanding of wasp-host genome interactions and supports HIM-mediated chromosomal integration as a possible mechanism of horizontal transfer from wasps to their hosts. IMPORTANCE Bracoviruses are endogenous domesticated viruses of parasitoid wasps that are injected together with wasp eggs into wasp host larvae during parasitism. Several studies have shown that some DNA circles packaged into bracovirus particles become integrated into host somatic genomes during parasitism, but the phenomenon has never been studied using nontargeted approaches. Here, we use bulk Illumina sequencing to systematically characterize and quantify bracovirus circle integrations that occur in four tissues of the Mediterranean corn borer (Sesamia nonagrioides) during parasitism by the Cotesia typhae wasp. Our analysis reveals that all circles containing a HIM integrate at substantial levels (from 12 to 85 integrations per host cell, in total) in all tissues, while other circles do not integrate. In addition to shedding new light on wasp-bracovirus-host interactions, our study supports HIM-mediated chromosomal integration of bracovirus as a possible source of wasp-to-host horizontal transfer, with long-term evolutionary consequences.
Keywords: bracovirus; chromosomal integration; genomics; horizontal transfer; host-parasite relationship; parasitoid wasps; polydnavirus.
Figures
References
-
- Gauthier J, Boulain H, van Vugt JJFA, Baudry L, Persyn E, Aury J-M, Noel B, Bretaudeau A, Legeai F, Warris S, Chebbi MA, Dubreuil G, Duvic B, Kremer N, Gayral P, Musset K, Josse T, Bigot D, Bressac C, Moreau S, Periquet G, Harry M, Montagné N, Boulogne I, Sabeti-Azad M, Maïbèche M, Chertemps T, Hilliou F, Siaussat D, Amselem J, Luyten I, Capdevielle-Dulac C, Labadie K, Merlin BL, Barbe V, de Boer JG, Marbouty M, Cônsoli FL, Dupas S, Hua-Van A, Le Goff G, Bézier A, Jacquin-Joly E, Whitfield JB, Vet LEM, Smid HM, Kaiser L, Koszul R, Huguet E, Herniou EA, Drezen JM. 2021. Chromosomal scale assembly of parasitic wasp genome reveals symbiotic virus colonization. Commun Biol 4:104–115. 10.1038/s42003-020-01623-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharanowski BJ, Ridenbaugh RD, Piekarski PK, Broad GR, Burke GR, Deans AR, Lemmon AR, Moriarty Lemmon EC, Diehl GJ, Whitfield JB, Hines HM. 2021. Phylogenomics of Ichneumonoidea (Hymenoptera) and implications for evolution of mode of parasitism and viral endogenization. Mol Phylogenet Evol 156:107023. 10.1016/j.ympev.2020.107023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

