Manipulating the exposome to enable better ageing
- PMID: 34319404
- PMCID: PMC8331090
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20200958
Manipulating the exposome to enable better ageing
Abstract
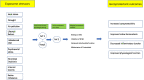
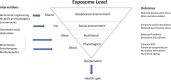
The sum total of life course exposures creates an exposome that has a significant impact on age-related health. Understanding the interplay between exposome factors and the (epi) genome, offers pertinent insights into the ageing process and its relationship with the accumulation of allostatic load. We propose to exploit this to develop a biomimetic approach that will provide insight into how evolution through natural selection in other species has solved many age related human health issues. In particular, we will emphasise the need to reconnect a more mechanistic approach to medical science with a broader natural sciences approach, using biomimetics to mitigate the global burden of age related ill health. In particular, we will discuss how such an approach indicates leverage of the activities of the Nrf 2 gene to enhance health span via reintroduction of the classical 'Food as Medicine' concept, including modulation of the microbiome and the creation of more salutogenic and biophilic environments. Additionally, we will discuss how this approach integrates with novel and developing senotherapies.
Keywords: Nrf2; ageing; allostatic load; biomimetics; exposome; microbiome.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.S. serves on a Scientific Advisory Board for REATA. R.J.J. has equity in XORTX Therapeutics and Colorado Research Partners, LLC. P.G.S. is in receipt of research awards form 4D Pharma and Constant Pharma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allostatic load and ageing: linking the microbiome and nutrition with age-related health.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Aug 30;47(4):1165-1172. doi: 10.1042/BST20190110. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31416886 Review.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Exposome of Ageing.Subcell Biochem. 2023;103:79-94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26576-1_5. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37120465
-
Ageing Trajectories: Exposome-Driven Pathobiological Mechanisms and Implications for Prevention from Blue Zones and Italian Longevity Hotspots Such as Cilento and Sicilian Mountain Villages.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4796. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104796. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cosmoses, one universe: a narrative review exploring the gut microbiome's role in the effect of urban risk factors on vascular ageing.Maturitas. 2024 Jun;184:107951. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2024.107951. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Maturitas. 2024. PMID: 38471294 Review.
-
Each meal matters in the exposome: Biological and community considerations in fast-food-socioeconomic associations.Econ Hum Biol. 2017 Nov;27(Pt B):328-335. doi: 10.1016/j.ehb.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Econ Hum Biol. 2017. PMID: 29107462
Cited by
-
Growth Performance and Fecal Microbiota of Dairy Calves Supplemented with Autochthonous Lactic Acid Bacteria as Probiotics in Mexican Western Family Dairy Farming.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 7;13(18):2841. doi: 10.3390/ani13182841. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760240 Free PMC article.
-
What Can the Gut Microbiota of Animals Teach Us about the Relationship between Nutrition and Burden of Lifestyle Diseases?Nutrients. 2024 Jun 6;16(11):1789. doi: 10.3390/nu16111789. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvesicle-Mediated Tissue Regeneration Mitigates the Effects of Cellular Ageing.Cells. 2023 Jun 23;12(13):1707. doi: 10.3390/cells12131707. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443741 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Environment and Aging Research: Opportunities for Synergy and Acceleration.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 21;14:824921. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.824921. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35264945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geroscience and climate science: Oppositional or complementary?Aging Cell. 2023 Aug;22(8):e13890. doi: 10.1111/acel.13890. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 37264538 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

