The potential role of neopterin in Covid-19: a new perspective
- PMID: 34319496
- PMCID: PMC8317144
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-021-04232-z
The potential role of neopterin in Covid-19: a new perspective
Abstract
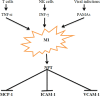
Neopterin (NPT) is a member of pteridines group, synthesized by macrophages when stimulated by interferon gamma (INF-γ). NPT is regarded as a macrophage stimulation indicator, marker of cellular immune activation and T helper 1 (Th1) type 1 immune response. Here, we aimed to provide a view point on the NPT features and role in Covid-19. Serum NPT level is regarded as an independent prognostic factor for Covid-19 severity, with levels starting to increase from the 3rd day of SARS-CoV-2 infection, being associated with severe dyspnea, longer hospitalization period and complications. Also, early raise of NPT reflects monocytes/macrophages activation before antibody immune response, despite the NPT level may also remain high in Covid-19 patients or at the end of incubation period before the onset of clinical symptoms. On the other hand, NPT attenuates the activity of macrophage foam cells and is linked to endothelial inflammation through inhibition of adhesion molecules and monocytes migration. However, NPT also exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects by suppressing NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasomes. NPT can be viewed as a protective compensatory mechanism to counterpoise hyper-inflammation, oxidative stress, and associated organ damage.
Keywords: Covid-19 severity; Neopterin; SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The importance of neopterin in COVID-19: The prognostic value and relation with the disease severity.Clin Biochem. 2022 Jun;104:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2022.03.002. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Clin Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35307400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic role of neopterin in COVID-19 patients.J Med Virol. 2021 Mar;93(3):1520-1525. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26472. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32860465
-
Evaluation of serum neopterin levels in severe COVID-19 patients: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 26;103(30):e38996. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038996. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39058886 Free PMC article.
-
Serum neopterin levels in relation to mild and severe COVID-19.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Dec 10;20(1):942. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05671-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33302893 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Mimics Pulmonary Dysfunction in Muscular Dystrophy as a Post-Acute Syndrome in Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 24;24(1):287. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010287. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A non-targeted metabolomics comparative study on plasma of pfizer and sinopharm COVID-19 vaccinated individuals, assessed by (TIMS-QTOF) mass spectrometry.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 30;10(15):e35443. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35443. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170395 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease Risk and Hyperhomocysteinemia: The Possible Link.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Aug;43(6):2743-2759. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01350-8. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37074484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mixed storm in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A narrative review and new term in the Covid-19 era.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Apr;11(4):e838. doi: 10.1002/iid3.838. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37102645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neopterin production in relation to COVID-19 in the Haut-Ogooué Province, Gabon.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):872. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09766-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39198763 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and functional findings in COVID-19 lung disease as compared to Pneumonia, ARDS, and High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;309:104000. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2022.104000. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36460252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Naimi MS, Lungnier CM, Al-Gareeb AI. Macrolides and COVID-19: an optimum premise. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2020;4(3):189. doi: 10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_103_20. - DOI
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Hussien NR, Al-Naimi MS, Al-Buhadily AK, Al-Gareeb AI, Lungnier C. Renin-Angiotensin system and fibrinolytic pathway in COVID-19: one-way skepticism. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2020;4(5):33.
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Niemi MS, Hussain NR, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Harchan NA, Al-Kurashi AH. The potential role of renin angiotensin system (RAS) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) in COVID-19: navigating the uncharted. In: Kibel A, editor. Selected chapters from the reninangiotensin system. London: IntechOpen; 2020. pp. 151–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

