Interactions between staphylococcal enterotoxins A and D and superantigen-like proteins 1 and 5 for predicting methicillin and multidrug resistance profiles among Staphylococcus aureus ocular isolates
- PMID: 34320020
- PMCID: PMC8318242
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254519
Interactions between staphylococcal enterotoxins A and D and superantigen-like proteins 1 and 5 for predicting methicillin and multidrug resistance profiles among Staphylococcus aureus ocular isolates
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and multidrug-resistant (MDR) S. aureus strains are well recognized as posing substantial problems in treating ocular infections. S. aureus has a vast array of virulence factors, including superantigens and enterotoxins. Their interactions and ability to signal antibiotics resistance have not been explored.
Objectives: To predict the relationship between superantigens and methicillin and multidrug resistance among S. aureus ocular isolates.
Methods: We used a DNA microarray to characterize the enterotoxin and superantigen gene profiles of 98 S. aureus isolates collected from common ocular sources. The outcomes contained phenotypic and genotypic expressions of MRSA. We also included the MDR status as an outcome, categorized as resistance to three or more drugs, including oxacillin, penicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, moxifloxacin, tetracycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and gentamicin. We identified gene profiles that predicted each outcome through a classification analysis utilizing Random Forest machine learning techniques.
Findings: Our machine learning models predicted the outcomes accurately utilizing 67 enterotoxin and superantigen genes. Strong correlates predicting the genotypic expression of MRSA were enterotoxins A, D, J and R and superantigen-like proteins 1, 3, 7 and 10. Among these virulence factors, enterotoxin D and superantigen-like proteins 1, 5 and 10 were also significantly informative for predicting both MDR and MRSA in terms of phenotypic expression. Strong interactions were identified including enterotoxins A (entA) interacting with superantigen-like protein 1 (set6-var1_11), and enterotoxin D (entD) interacting with superantigen-like protein 5 (ssl05/set3_probe 1): MRSA and MDR S. aureus are associated with the presence of both entA and set6-var1_11, or both entD and ssl05/set3_probe 1, while the absence of these genes in pairs indicates non-multidrug-resistant and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus.
Conclusions: MRSA and MDR S. aureus show a different spectrum of ocular pathology than their non-resistant counterparts. When assessing the role of enterotoxins in predicting antibiotics resistance, it is critical to consider both main effects and interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
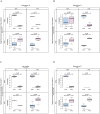
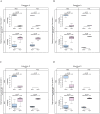
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage, virulence traits, antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and genetic lineages in healthy humans in Spain, with detection of CC398 and CC97 strains.Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Aug;301(6):500-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 May 12. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21570348
-
Multidrug-resistant clones of community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Chinese children and the resistance genes to clindamycin and mupirocin.J Med Microbiol. 2012 Sep;61(Pt 9):1240-1247. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.042663-0. Epub 2012 May 17. J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22595913
-
Clinical features, epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and exotoxin genes (including that of Panton-Valentine leukocidin) of gentamicin-susceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (GS-MRSA) isolated at a paediatric teaching hospital in New South Wales, Australia.Pathology. 2008 Jan;40(1):64-71. doi: 10.1080/00313020701716276. Pathology. 2008. PMID: 18038318
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a controversial food-borne pathogen.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017 Jun;64(6):409-418. doi: 10.1111/lam.12735. Epub 2017 May 3. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28304109 Review.
-
Secreted virulence factor comparison between methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, and its relevance to atopic dermatitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jan;125(1):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.039. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20109735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
First study on diversity and antimicrobial-resistant profile of staphylococci in sports animals of Southern Thailand.Vet World. 2022 Mar;15(3):765-774. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.765-774. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Vet World. 2022. PMID: 35497942 Free PMC article.
-
Access to care through telehealth among U.S. Medicare beneficiaries in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 6;10:946944. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.946944. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36148338 Free PMC article.
-
Global insights into MRSA bacteremia: a bibliometric analysis and future outlook.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 22;15:1516584. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1516584. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39911705 Free PMC article.
-
Telehealth utilization in U.S. medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older during the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Public Health. 2023 Feb 20;23(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15263-0. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36803677 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Infectious and Non-Infectious Ocular Conditions.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;11(8):1011. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081011. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abolghait SK, Fathi AG, Youssef FM, Algammal AM. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from chicken meat and giblets often produces staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) in non-refrigerated raw chicken livers. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 2020;328:108669. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108669 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Enany ME, Algammal AM, Shagar GI, Hanora AM, Elfeil WK, Elshaffy NM. Molecular typing and evaluation of Sidr honey inhibitory effect on virulence genes of MRSA strains isolated from catfish in Egypt. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2018;31(5). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

