Effectiveness of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination Against Penile HPV Infection in Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women
- PMID: 34320185
- PMCID: PMC8842819
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab390
Effectiveness of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination Against Penile HPV Infection in Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women
Abstract
Background: In the United States, human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination has been recommended since 2011 for boys aged 11-12 years, with catch-up vaccination recommended through age 26 years for previously unvaccinated men who have sex with men (MSM).
Methods: During 2016-2018, a cross-sectional study enrolled MSM and transgender women aged 18-26 years in Seattle, Washington. Participants submitted self-collected penile swab specimens for HPV genotyping. HPV vaccination history was self-reported. We compared HPV prevalence among vaccinated participants with that in participants with no or unknown vaccination history, using log-binomial regression to estimate adjusted prevalence ratios and confidence intervals.
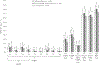
Results: Among 687 participants, 348 (50.7%) self-reported ever receiving ≥1 HPV vaccine dose; the median age at first HPV vaccination was 21 years, and the median age at first sex, 17 years. Overall, the prevalence of penile quadrivalent HPV vaccine (4vHPV)-type HPV was similar in vaccinated participants (12.1%) and participants with no or unknown vaccination (15.6%) (adjusted prevalence ratio, 0.69 [95% confidence interval, .47-1.01]). However, the prevalence was significantly lower in participants vaccinated at age ≤18 years than in those with no of unknown vaccination (0.15 [.04-.62]), corresponding to a vaccine effectiveness of 85% against 4vHPV-type HPV.
Conclusions: Results suggest that HPV vaccination is effective in preventing penile HPV infections in young MSM when administered at age ≤18 years.
Keywords: papillomavirus infections; papillomavirus vaccines; sexual and gender minorities; vaccination.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Marra E, Lin C, Clifford GM. Type-specific anal human papillomavirus prevalence among men, according to sexual preference and HIV status: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect Dis 2019; 219:590–8. - PubMed
-
- Machalek DA, Poynten M, Jin F, et al. Anal human papillomavirus infection and associated neoplastic lesions in men who have sex with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13:487–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

