Breast and Prostate Cancer Risks for Male BRCA1 and BRCA2 Pathogenic Variant Carriers Using Polygenic Risk Scores
- PMID: 34320204
- PMCID: PMC8755508
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djab147
Breast and Prostate Cancer Risks for Male BRCA1 and BRCA2 Pathogenic Variant Carriers Using Polygenic Risk Scores
Abstract
Background: Recent population-based female breast cancer and prostate cancer polygenic risk scores (PRS) have been developed. We assessed the associations of these PRS with breast and prostate cancer risks for male BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variant carriers.
Methods: 483 BRCA1 and 1318 BRCA2 European ancestry male carriers were available from the Consortium of Investigators of Modifiers of BRCA1/2 (CIMBA). A 147-single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) prostate cancer PRS (PRSPC) and a 313-SNP breast cancer PRS were evaluated. There were 3 versions of the breast cancer PRS, optimized to predict overall (PRSBC), estrogen receptor (ER)-negative (PRSER-), or ER-positive (PRSER+) breast cancer risk.
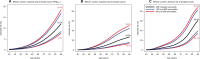
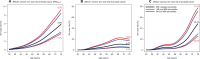
Results: PRSER+ yielded the strongest association with breast cancer risk. The odds ratios (ORs) per PRSER+ standard deviation estimates were 1.40 (95% confidence interval [CI] =1.07 to 1.83) for BRCA1 and 1.33 (95% CI = 1.16 to 1.52) for BRCA2 carriers. PRSPC was associated with prostate cancer risk for BRCA1 (OR = 1.73, 95% CI = 1.28 to 2.33) and BRCA2 (OR = 1.60, 95% CI = 1.34 to 1.91) carriers. The estimated breast cancer odds ratios were larger after adjusting for female relative breast cancer family history. By age 85 years, for BRCA2 carriers, the breast cancer risk varied from 7.7% to 18.4% and prostate cancer risk from 34.1% to 87.6% between the 5th and 95th percentiles of the PRS distributions.
Conclusions: Population-based prostate and female breast cancer PRS are associated with a wide range of absolute breast and prostate cancer risks for male BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers. These findings warrant further investigation aimed at providing personalized cancer risks for male carriers and informing clinical management.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Comment in
-
Urological Oncology: Prostate Cancer.J Urol. 2022 Mar;207(3):735-738. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002377. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 34915718 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rizzolo P, Silvestri V, Tommasi S, et al. Male breast cancer: genetics, epigenetics, and ethical aspects. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(suppl 8):viii75–viii82. - PubMed

