Dysregulated oxalate metabolism is a driver and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34320345
- PMCID: PMC8363062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109420
Dysregulated oxalate metabolism is a driver and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis
Abstract
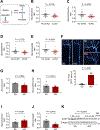
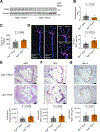
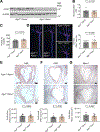
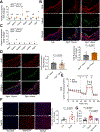
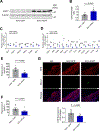
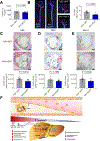
Dysregulated glycine metabolism is emerging as a common denominator in cardiometabolic diseases, but its contribution to atherosclerosis remains unclear. In this study, we demonstrate impaired glycine-oxalate metabolism through alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGXT) in atherosclerosis. As found in patients with atherosclerosis, the glycine/oxalate ratio is decreased in atherosclerotic mice concomitant with suppression of AGXT. Agxt deletion in apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe-/-) mice decreases the glycine/oxalate ratio and increases atherosclerosis with induction of hepatic pro-atherogenic pathways, predominantly cytokine/chemokine signaling and dysregulated redox homeostasis. Consistently, circulating and aortic C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) and superoxide in lesional macrophages are increased. Similar findings are observed following dietary oxalate overload in Apoe-/- mice. In macrophages, oxalate induces mitochondrial dysfunction and superoxide accumulation, leading to increased CCL5. Conversely, AGXT overexpression in Apoe-/- mice increases the glycine/oxalate ratio and decreases aortic superoxide, CCL5, and atherosclerosis. Our findings uncover dysregulated oxalate metabolism via suppressed AGXT as a driver and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis.
Keywords: AGXT; CCL5; amino acids; atherosclerosis; glycine; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxalate.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Arafa A, Eshak ES, and Iso H (2020). Oxalates, urinary stones and risk of cardiovascular diseases. Med. Hypotheses 137:109570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HL150233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147527/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL145131/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141155/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098435/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL150233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106540/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL137214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145176/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138094/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK110768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

