Staphylococcus aureus uses the ArlRS and MgrA cascade to regulate immune evasion during skin infection
- PMID: 34320352
- PMCID: PMC8450000
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109462
Staphylococcus aureus uses the ArlRS and MgrA cascade to regulate immune evasion during skin infection
Abstract
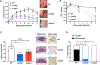
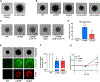
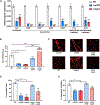
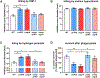
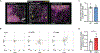
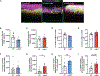
Skin is one of the most common sites of host immune response against Staphylococcus aureus infection. Here, through a combination of in vitro assays, mouse models, and intravital imaging, we find that S. aureus immune evasion in skin is controlled by a cascade composed of the ArlRS two-component regulatory system and its downstream effector, MgrA. S. aureus lacking either ArlRS or MgrA is less virulent and unable to form correct abscess structure due to de-repression of a giant surface protein, Ebh. These S. aureus mutants also have decreased expression of immune evasion factors (leukocidins, chemotaxis-inhibitory protein of S. aureus [CHIPS], staphylococcal complement inhibitor [SCIN], and nuclease) and are unable to kill neutrophils, block their chemotaxis, degrade neutrophil extracellular traps, and survive direct neutrophil attack. The combination of disrupted abscess structure and reduced immune evasion factors makes S. aureus susceptible to host defenses. ArlRS and MgrA are therefore the main regulators of S. aureus immune evasion and promising treatment targets.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; abscess; gene regulation; immune evasion; innate immunity; intravital microscopy; neutrophil; skin infection; surface proteins.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Baba T, Takeuchi F, Kuroda M, Yuzawa H, Aoki K, Oguchi A, Nagai Y, Iwama N, Asano K, Naimi T, et al. (2002). Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359, 1819–1827. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Zhu X, Zhao K, Yan Y, Xu T, Wang J, Zheng J, Huang W, Shi L, Shang Y, et al. (2019). The role of ArlRS in regulating oxacillin susceptibility in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus indicates it is a potential target for antimicrobial resistance breakers. Emerg. Microbes Infect 8, 503–515. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M, Carnelutti A, and Righi E (2017). The role of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in skin and soft tissue infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis 30, 150–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

