On the PHLPPside: Emerging roles of PHLPP phosphatases in the heart
- PMID: 34320369
- PMCID: PMC8403656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110097
On the PHLPPside: Emerging roles of PHLPP phosphatases in the heart
Abstract
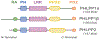
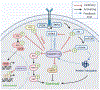
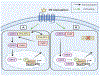
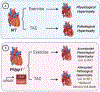
PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase (PHLPP) is a family of enzymes made up of two isoforms (PHLPP1 and PHLPP2), whose actions modulate intracellular activity via the dephosphorylation of specific serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) residues on proteins such as Akt. Recent data generated in our lab, supported by findings from others, implicates the divergent roles of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 in maintaining cellular homeostasis since dysregulation of these enzymes has been linked to various pathological states including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, ischemia/reperfusion injury, musculoskeletal disease, and cancer. Therefore, development of therapies to modulate specific isoforms of PHLPP could prove to be therapeutically beneficial in several diseases especially those targeting the cardiovascular system. This review is intended to provide a comprehensive summary of current literature detailing the role of the PHLPP isoforms in the development and progression of heart disease.
Keywords: Akt; Cardiac hypertrophy; Cardiovascular disease; PHLPP; Phosphatase; Serine/threonine.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
None.
Figures

References
-
- Gao T, Furnari F, and Newton AC, PHLPP: a phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis, and suppresses tumor growth. Mol Cell, 2005. 18(1): p. 13–24. - PubMed
-
- Kamada R, et al. , Metal-dependent Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PPM family: Evolution, structures, diseases and inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther, 2020. 215: p. 107622. - PubMed
-
- Brognard J, et al. , PHLPP and a second isoform, PHLPP2, differentially attenuate the amplitude of Akt signaling by regulating distinct Akt isoforms. Mol Cell, 2007. 25(6): p. 917–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

