Selective activation of PFKL suppresses the phagocytic oxidative burst
- PMID: 34320407
- PMCID: PMC8802628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.004
Selective activation of PFKL suppresses the phagocytic oxidative burst
Abstract
In neutrophils, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) generated via the pentose phosphate pathway fuels NADPH oxidase NOX2 to produce reactive oxygen species for killing invading pathogens. However, excessive NOX2 activity can exacerbate inflammation, as in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Here, we use two unbiased chemical proteomic strategies to show that small-molecule LDC7559, or a more potent designed analog NA-11, inhibits the NOX2-dependent oxidative burst in neutrophils by activating the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 liver type (PFKL) and dampening flux through the pentose phosphate pathway. Accordingly, neutrophils treated with NA-11 had reduced NOX2-dependent outputs, including neutrophil cell death (NETosis) and tissue damage. A high-resolution structure of PFKL confirmed binding of NA-11 to the AMP/ADP allosteric activation site and explained why NA-11 failed to agonize phosphofructokinase-1 platelet type (PFKP) or muscle type (PFKM). Thus, NA-11 represents a tool for selective activation of PFKL, the main phosphofructokinase-1 isoform expressed in immune cells.
Keywords: LDC7559; NA-11; NADPH; NETosis; NOX2; PFKL; ROS; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2021 Genentech Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests N.A., T.M., K.Y., Z.L., D.S., N.K., K.N., S.T.S., and V.M.D. are employees of Genentech.
Figures
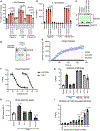

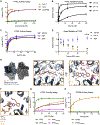
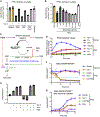

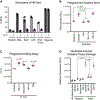
Comment in
-
Phagocyte metabolism: neutrophils have their cake but don't eat it.Trends Immunol. 2021 Oct;42(10):846-848. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.08.011. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34538594
References
-
- Amulic B, Cazalet C, Hayes GL, Metzler KD, and Zychlinsky A (2012). Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol 30, 459–489. - PubMed
-
- Andrés V, Carreras J, and Cussó R (1990). Regulation of muscle phosphofructokinase by physiological concentrations of bisphosphorylated hexoses: effect of alkalinization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 172, 328–334. - PubMed
-
- Banaszak K, Mechin I, Obmolova G, Oldham M, Chang SH, Ruiz T, Radermacher M, Kopperschlager G, and Rypniewski W (2011). The crystal structures of eukaryotic phosphofructokinases from baker’s yeast and rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Mol. Biol 407, 284–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

