IgE and IgG4 Repertoire in Asymptomatic HDM-Sensitized and HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Patients
- PMID: 34320489
- PMCID: PMC8743936
- DOI: 10.1159/000517824
IgE and IgG4 Repertoire in Asymptomatic HDM-Sensitized and HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Patients
Abstract
Introduction: Asymptomatic sensitization is defined as the presence of positive skin prick test (SPT) and/or positive serum allergen-specific IgE in the absence of clinical allergic symptoms. Currently, there is no convincing explanation why some people with positive allergen tests do not show symptoms. We aimed to investigate the house dust mite (HDM)-specific IgE and IgG4 repertoire in asymptomatic HDM-sensitized subjects and HDM-induced allergic rhinitis (AR) patients.
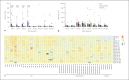
Methods: A total of 48 subjects sensitized to HDM were included in this study: 27 had AR with/without asthma (symptomatic group), and 21 had no allergic symptoms (asymptomatic group). Six healthy individuals served as control group. Peripheral blood samples were collected for serum IgE and IgG4 assay and basophil activation tests (BATs). IgE and IgG4 assay included antibodies to Dermatophagoides (Der) p1, 2, 7, 10, 21, 23, and Der f1, 2.
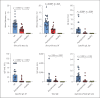
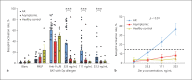
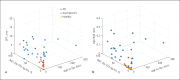
Results: AR patients had a larger wheal diameter of SPT (7.0 vs. 3.0 mm, p < 0.0001) and a higher specific IgE to Der p (15.50 vs. 0.70 KU/L, p < 0.0001) than asymptomatic subjects. They also showed more frequent sensitization to Der p1 and Der p2 (both p < 0.05). However, the total IgE and specific IgG4 did not differ significantly between the 2 groups. The basophil activation response after being stimulated with HDM was observed to be higher in AR patients (all p < 0.05).
Conclusions: There are differences in SPT, serum-specific IgE to Der p, component allergen Der p1 and Der p2 level and BAT between AR patients and asymptomatic subjects sensitized to HDM. IgG4 alone cannot differentiate asymptomatic individuals from AR patients.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Asymptomatic sensitization; Basophil activation; House dust mite; House dust mite component.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu R, Wang J, Wu Y, Yang Y, Huang N, Yang Y, et al. The allergic rhinitis control test questionnaire is valuable in guiding step-down pharmacotherapy treatment of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7((1)):272–8. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Hellings PW, Agache I, Amat F, Annesi-Maesano I, Ansotegui IJ, et al. Mobile Airways Sentinel Network (MASK) Study Group. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) Phase 4 (2018) change management in allergic rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using mobile technology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143((3)):864–79. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization GA(2)LEN and AllerGen) Allergy. 2008;63((Suppl 86)):8–160. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

