Combination of rapamycin and SAHA enhanced radiosensitization by inducing autophagy and acetylation in NSCLC
- PMID: 34321364
- PMCID: PMC8351722
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203226
Combination of rapamycin and SAHA enhanced radiosensitization by inducing autophagy and acetylation in NSCLC
Abstract
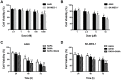
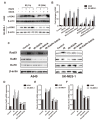
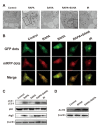
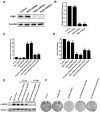
Radiotherapy plays an essential role in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, cancer cells' resistance to ionizing radiation (IR) is the primary reason for radiotherapy failure leading to tumor relapse and metastasis. DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) repair after IR is the primary mechanism of radiotherapy resistance. In this study, we investigated the effects of autophagy-inducing agent, Rapamycin (RAPA), combined with the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA), on the radiosensitivity of A549 and SK-MES-1 cells, and examined the combination effects on DNA damage repair, and determined the level of autophagy and acetylation in A549 cells. We also investigated the combination treatment effect on the growth of A549 xenografts after radiotherapy, and the level of DNA damage, autophagy, and acetylation. Our results showed that RAPA combined with SAHA significantly increased the inhibitory effect of radiotherapy compared with the single treatment group. The combined treatment increased the expression of DNA damage protein γ-H2AX and decreased DNA damage repair protein expression. RAPA combined with SAHA was induced mainly by regulating acetylation levels and autophagy. The effect of combined treatment to increase radiotherapy sensitivity will be weakened by inhibiting the level of autophagy. Besides, the combined treatment also showed a significantly inhibited tumor growth in the A549 xenograft model. In conclusion, these results identify a potential therapeutic strategy of RAPA combined with SAHA as a radiosensitizer to decreased DSB repair and enhanced DNA damage by inducing acetylation levels and autophagy for NSCLC.
Keywords: DNA damage; autophagy; histone deacetylase inhibitor; radiation; rapamycin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined Effects of Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid and Cisplatin on Radiation Sensitivity and Cancer Cell Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 May;15(5):842-53. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0445. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26839308
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, enhances radiosensitivity and suppresses lung metastasis in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e76340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076340. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130769 Free PMC article.
-
A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor exhibits antitumor activity via apoptosis induction, F-actin disruption and gene acetylation in lung cancer.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 14;5(9):e12417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012417. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20856855 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation: a novel link between double-strand break repair and autophagy.Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 15;72(6):1332-5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3172. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22422989 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors as radiosensitisers: effects on DNA damage signalling and repair.Br J Cancer. 2013 Mar 5;108(4):748-54. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.21. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23361058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autoimmunity and Carcinogenesis: Their Relationship under the Umbrella of Autophagy.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 8;11(4):1130. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041130. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Lung Cancer Treatment with Combined c-Met Promoter-Driven Oncolytic Adenovirus and Rapamycin.Cells. 2024 Sep 23;13(18):1597. doi: 10.3390/cells13181597. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329778 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring a novel seven-gene marker and mitochondrial gene TMEM38A for predicting cervical cancer radiotherapy sensitivity using machine learning algorithms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 24;14:1302074. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1302074. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38327905 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of apoptosis, autophagy and ferroptosis by non-coding RNAs in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):352. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11279. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35493430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of autophagy‑modulating long non‑coding RNAs in tumor radioresistance (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Nov;54(5):142. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8975. Epub 2025 Aug 24. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40849822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

