Bilateral Congenital Ptosis Associated with Optic Disc Melanocytoma
- PMID: 34321824
- PMCID: PMC8270015
- DOI: 10.4103/meajo.MEAJO_543_20
Bilateral Congenital Ptosis Associated with Optic Disc Melanocytoma
Abstract
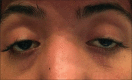
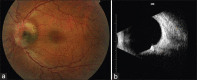
We report a rare clinical association of optic disc melanocytoma (ODM) occurring with bilateral congenital ptosis that has not been previously reported. A 28-year-old male patient presented with bilateral congenital ptosis. On examination, his vision was 20/20 in each eye, and dilated fundus examination indicated a pigmented lesion over the left inferior temporal aspect of the optic disc that was consistent with an optic nerve melanocytoma. B-scan ultrasonography indicated a calcified elevated optic nerve head. Bilateral frontalis sling procedures were performed for congenital ptosis with satisfactory results at 1 year postoperatively. There was no progression of the lesion in the left eye. Knowing the key ophthalmoscopic features of an ODM can aid in diagnosing this lesion; ophthalmologists should be familiar with this lesion in addition to the rare association of ptosis. Affected patients should be periodically assessed.
Keywords: Congenital; melanocytoma; optic disc; ptosis.
Copyright: © 2021 Middle East African Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shields JA, Demirci H, Mashayekhi A, Shields CL. Melanocytoma of optic disc in 115 cases: The 2004 Samuel Johnson Memorial Lecture, Part 1. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1739–46. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman LE, Garron LK. Melanocytoma of the optic disc. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1962;2:431–40.
-
- Sharma H, Puri LR. Melanocytoma of the optic disc – A case report. Nepal J Ophthalmol. 2012;4:323–5. - PubMed
-
- Rishi P, Venkatesh R. Central retinal artery occlusion secondary to optic disk melanocytoma. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2012;6:212–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

