Endoscopic submucosal dissection vs endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal polyps: A meta-analysis and meta-regression with single arm analysis
- PMID: 34321855
- PMCID: PMC8291020
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3925
Endoscopic submucosal dissection vs endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal polyps: A meta-analysis and meta-regression with single arm analysis
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has shown to be effective in management of colorectal neoplasm in the Asian countries, while its implementation in Western countries where endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is preferred is still debatable.
Aim: To compare the surgical, histological, and oncological outcomes between ESD and EMR in the treatment of colorectal polyps, with subgroup analysis comparing the efficacy of ESD and EMR between Japan and the rest of the world.
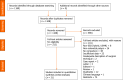
Methods: Embase and Medline databases were searched from inception to October 2020 in accordance with PRISMA guidelines for studies comparing en bloc, complete resection, margin involvement, resection time, need for additional surgery, complications, and recurrence rate of ESD with EMR.
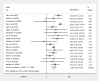
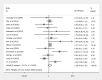
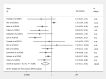
Results: Of 281344 colorectal polyps from 21 studies were included. When compared to EMR, the pooled analysis revealed ESD was associated with higher en bloc and complete resection rate, and lower lateral margin involvement and recurrence. ESD led to increased procedural time, need for additional surgery, and perforation risk. No significant difference in bleeding risk was found between the two groups. Meta-regression analysis suggested only right colonic polyps correlated with an increased perforation risk in ESD. Confounders including polyp size and invasion depth did not significantly influence the en bloc and complete resection rate, bleeding risk and recurrence. In subgroup analysis, Japan performed better than the rest of the world in both ESD and EMR with perforation risk of 4% and 0.0002%, respectively, as compared to perforation risk of 8% and 1%, respectively, in reports coming from rest of the world.
Conclusion: ESD resulted in better resection outcomes and lower recurrence compared to EMR. With appropriate training, ESD is preferred over EMR as the first-line therapy for resection of colorectal polyps, without restricting to lesions greater than 20 mm and those with high suspicion of submucosal invasion.
Keywords: Colonic polyps; Colonoscopy; Colorectal neoplasm; Endoscopic mucosal resection; Endoscopy.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors deny any conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for rectal carcinoid tumor. A meta-analysis and meta-regression with single-arm analysis.J Dig Dis. 2021 Oct;22(10):562-571. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.13048. J Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 34472210 Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic mucosal resection vs endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal sessile/non-polypoid lesions.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2022 Aug;31(6):835-847. doi: 10.1080/13645706.2022.2032759. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2022. PMID: 35112654
-
Endoscopic mucosal resection versus endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumors: a meta-analysis.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2020 Dec;112(12):941-947. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6681/2019. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2020. PMID: 33207885
-
Comparison of endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for large colorectal tumors.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Nov;23(11):1042-9. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32834aa47b. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21869682
-
Tip-in endoscopic mucosal resection for large colorectal sessile polyps.Surg Endosc. 2021 Apr;35(4):1820-1826. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07581-w. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Surg Endosc. 2021. PMID: 32356110
Cited by
-
Clinical analysis of metastatic characteristics of infrapyloric lymph nodes (No.206) and terminal ileum lymph nodes in patients with right colon cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Oct 22;19(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02414-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34674722 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter evaluation of recurrence in endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection in the colon: A Western perspective.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Jun 16;15(6):458-468. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v15.i6.458. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37397977 Free PMC article.
-
A staged approach to resecting a large rectal polyp using endoscopic mucosal resection and trans-anal endoscopic microsurgery: a case report.J Surg Case Rep. 2025 Feb 19;2025(2):rjaf068. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjaf068. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39975845 Free PMC article.
-
Algorithmic approach for endoscopic management of colorectal polyps: an up-to-date review.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025;18(1):39-52. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v18i1.3085. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025. PMID: 40734813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of complications related to colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection.Clin Endosc. 2023 Jul;56(4):423-432. doi: 10.5946/ce.2023.104. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Clin Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37501624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, O'Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, Waye JD, Schapiro M, Bond JH, Panish JF. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1977–1981. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:145–164. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto H, Yube T, Isoda N, Sato Y, Sekine Y, Higashizawa T, Ido K, Kimura K, Kanai N. A novel method of endoscopic mucosal resection using sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;50:251–256. - PubMed
-
- Pimentel-Nunes P, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Ponchon T, Repici A, Vieth M, De Ceglie A, Amato A, Berr F, Bhandari P, Bialek A, Conio M, Haringsma J, Langner C, Meisner S, Messmann H, Morino M, Neuhaus H, Piessevaux H, Rugge M, Saunders BP, Robaszkiewicz M, Seewald S, Kashin S, Dumonceau JM, Hassan C, Deprez PH. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2015;47:829–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

