Quantifying the survival benefit of completing all the six cycles of radium-223 therapy in patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer with predominant bone metastases
- PMID: 34321965
- PMCID: PMC8286012
- DOI: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_74_20
Quantifying the survival benefit of completing all the six cycles of radium-223 therapy in patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer with predominant bone metastases
Abstract
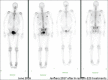
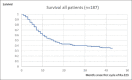
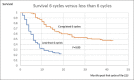
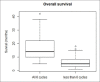
A retrospective analysis was performed of epidemiological data assessing the survival of patients who had received radium-223 for castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer treated at a regional tertiary referral center over a 5-year period. The patients' age, date of first treatment, and the number of cycles of radium-223 given were obtained from the patients' electronic patient record (EPR). Data on the date of death were provided by national death registrations which update the EPR via a unique national health service number. A total of 187 patients (mean age on the date of first treatment: 73 years; range: 56-93) were treated from April 1, 2014, to June 30, 2019. The median overall survival of the 119 patients (71%) who had died by December 31, 2019, was 15 months. There was no significant age difference between those who had died and survivors (72 vs. 74 years). On a further analysis, it was found that the median overall survival of the 107 patients who had received all the six cycles of radium-223 was 31 months, significantly longer than the median overall survival of only 6 months for those eighty patients who had received less than the full course of six cycles of radium-223 (P = 0.001). Of those who received all the six cycles of treatment, 58 patients had died (58%) and the 1-year survival was 87%. This was compared to the group of patients receiving <6 cycles of radium-223 where 61 patients (76%) had died and the 1-year survival was 30%. Therefore, the hazard ratio of dying before 1 year if the patient did not receive all the six cycles of treatment was 2.9. Where the reason for stopping treatment was recorded on the EPR the most common cause for the cessation of treatment was because of the side effects caused by the treatment itself. Other causes were hospitalization with comorbidities, disease progression, or patient choice. Given the survival advantage of receiving the full course of all the six cycles of treatment, this should be administered if possible and the patients should be managed in such a way as to allow the complete treatment course to be given.
Keywords: Carcinoma of the prostate; median overall survival; radium-223.
Copyright: © 2020 World Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world Outcomes and Factors Predicting Survival and Completion of Radium 223 in Metastatic Castrate-resistant Prostate Cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2018 Sep;30(9):548-555. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2018. PMID: 29934104
-
Radium-223 and concomitant therapies in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: an international, early access, open-label, single-arm phase 3b trial.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Sep;17(9):1306-16. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30173-5. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27473888 Clinical Trial.
-
Factors Influencing Outcome Post-Radium-223 Dichloride in Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Review of Some Real-World Challenges.World J Nucl Med. 2022 Sep 2;21(4):283-289. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1750015. eCollection 2022 Dec. World J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 36398304 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of radium-223 in prostate cancer.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015 May;11(5):843-9. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1021332. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25740232 Review.
-
Optimal usage of radium-223 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.J Formos Med Assoc. 2017 Nov;116(11):825-836. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29046247 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of the BIO-Ra Score in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with Radium-223 after the European Medicines Agency Restricted Use: Secondary Investigations of the Multicentric BIO-Ra Study.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 29;14(7):1744. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071744. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406515 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Nuclear Medicine in Prostate Cancer: Current State and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;15(19):4746. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194746. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world effectiveness, long-term safety and treatment pathway integration of radium-223 therapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 22;9:fmed-09-1070392. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1070392. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36619649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world utilization patterns and survival in men with metastatic prostate cancer treated with Radium-223 in the United States.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025 Apr 4. doi: 10.1038/s41391-025-00969-6. Online ahead of print. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. PMID: 40185917
-
Real-world patient characteristics associated with survival of 2 years or more after radium-223 treatment for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (EPIX study).Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022 Feb;25(2):306-313. doi: 10.1038/s41391-021-00488-0. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022. PMID: 35190653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharifi N, Dahut WL. Figg WD Secondary hormonal therapy for prostate cancer: What lies on the horizon? BJU Int. 2008;101:271–4. - PubMed
-
- Harzstark AL, Ryan CJ. Therapies in development for castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008;8:259–68. - PubMed
-
- Abouassaly R, Paciorek A, Ryan CJ, Carroll PR, Klein EA. Predictors of clinical metastasis in prostate cancer patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy: Results from CaPSURE. Cancer. 2009;115:4470–6. - PubMed
-
- Nightengale B, Brune M, Blizzard SP, Ashley-Johnson M, Slan S. Strontium chloride Sr 89 for treating pain from metastatic bone disease. J Health Syst Pharm. 1995;52:2189–95. - PubMed
-
- Cowan RJ, Chilton HM, Cooper MR, Ferree CR, Watson EE, Robinson RG. Hematologic depression following therapy with strontium-89 chloride. Clin Nucl Med. 1986;11:845–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

