The Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 34322012
- PMCID: PMC8311738
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.691512
The Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
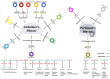
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are two neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) commonly found in elderly patients that are difficult to diagnose and lack effective treatment. Currently, the available diagnostic methods for these two NDDs do not meet clinical diagnostic expectations. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a diverse group of endogenous non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) found in eukaryotic cells. Emerging studies suggest that altered expression of circRNAs is involved in the pathological processes of NDDs. CircRNAs could also prove to be promising biomarkers for the early diagnosis of NDDs such as AD and PD. Growing evidence has improved our knowledge of the roles of circRNAs in NDDs, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches that target transcription for preventing neurodegeneration. In this review, we describe the formation mechanisms and functions of circRNAs as well as methods of validation. We also discuss the emerging role of circRNAs in the pathophysiology of AD and PD and their potential value as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for AD and PD in the future.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; biomarker; circular RNAs; pathophysiology; therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang and Bian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The clinical perspective of circular RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: potential diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Nov 18;18:1470641. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1470641. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39624645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanism of circular RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14499. doi: 10.1111/cns.14499. Epub 2023 Oct 21. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37864389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of circular RNAs in Parkinson's disease.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 16;17:1137363. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1137363. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36925739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs: New Insights in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 14;25(4):2268. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042268. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into the Role of CircRNAs: Biogenesis, Characterization, Functional, and Clinical Impact in Human Malignancies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 5;9:617281. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.617281. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33614648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of non‑coding RNAs as biomarkers and the application of omics technologies in Alzheimer's disease (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Jan;51(1):5. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5208. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36453246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA expression in ALS is progressively deregulated and tissue-dependent.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11725-4. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40596818 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Role of Non-coding RNAs in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1473:129-155. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-81908-7_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40128478 Review.
-
Context-Dependent Regulation of Gene Expression by Non-Canonical Small RNAs.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Apr 29;8(3):29. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8030029. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 35645336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating blood circular RNA in Parkinson's Disease; from involvement in pathology to diagnostic tools in at-risk individuals.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Nov 18;10(1):222. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00839-3. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39557914 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

