The ED50 and ED95 of Prophylactic Norepinephrine for Preventing Post-Spinal Hypotension During Cesarean Delivery Under Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia: A Prospective Dose-Finding Study
- PMID: 34322021
- PMCID: PMC8312548
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.691809
The ED50 and ED95 of Prophylactic Norepinephrine for Preventing Post-Spinal Hypotension During Cesarean Delivery Under Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia: A Prospective Dose-Finding Study
Abstract
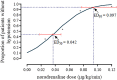
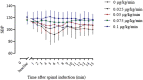
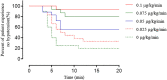
Background: Hypotension commonly occurs with spinal anesthesia during cesarean delivery. Norepinephrine is an alternative to phenylephrine which can be used to prevent or treat hypotension, with better maintained cardiac output and less bradycardia. However, an appropriate initial prophylactic infusion dose of norepinephrine remains unclear. The aim of this study was to describe the dose-response relationship of prophylactic norepinephrine infusion during cesarean delivery under combined spinal-epidural anesthesia. Methods: We performed a prospective, randomized, double-blinded dose-finding study. One hundred patients undergoing elective cesarean delivery were randomly assigned to receive an infusion of norepinephrine at 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075 or 0.1 μg/kg/min initiated immediately after intrathecal injection of 10 mg bupivacaine combined with 5 µg sufentanil. An effective dose was considered when there was no hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 90 mm Hg or < 80% of baseline) during the time period from injection of intrathecal local anesthetic to delivery of the neonate. The primary aim was to determine the dose-response relationship of norepinephrine to prevent spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension. The median effective dose (ED50) and 95% effective dose (ED95) for norepinephrine were calculated utilizing probit analysis. Results: The proportion of patients with hypotension was 80, 70, 40, 15 and 5% at norepinephrine doses of 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075 and 0.1 μg/kg/min, respectively. The ED50 and ED95 were 0.042 (95% CI, 0.025-0.053) µg/kg/min and 0.097 (95% CI, 0.081-0.134) µg/kg/min, respectively. There were no differences in the Apgar scores (p = 0.685) or umbilical arterial pH (p = 0.485) measurements of the newborns among the treatment groups. Conclusion: A norepinephrine infusion of 0.1 μg/kg/min as an initial starting dose was effective for the prevention of spinal-induced hypotension.
Keywords: anesthesia; cesarean delivery; hypotension; norepinephrine; spinal.
Copyright © 2021 Xu, Drzymalski, Ai, Yao, Liu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic intravenous norepinephrine for the prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean section: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1247214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1247214. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37795034 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine for the prevention of spinal-induced hypotension during caesarean delivery under combined spinal-epidural anaesthesia: Randomised, double-blind, dose-finding study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2020 Apr;37(4):309-315. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001152. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 31977628 Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous initial bolus during prophylactic norepinephrine infusion to prevent spinal hypotension for cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled, dose-finding trial.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Oct;97:111562. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111562. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39047530 Clinical Trial.
-
ED50 and ED95 of intrathecal hyperbaric ropivacaine for parturients undergoing cesarean section with prophylactic infusion of phenylephrine: A Prospective dose-finding Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(50):e13727. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013727. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30558092 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Minimum Effective Dose (ED50 and ED95) of Intrathecal Hyperbaric Bupivacaine for Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review.AANA J. 2018 Oct;86(5):348-360. AANA J. 2018. PMID: 31584404
Cited by
-
Prophylactic intravenous norepinephrine for the prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean section: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1247214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1247214. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37795034 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic infusion of norepinephrine does not affect the rostral spread of spinal anesthesia in pregnancy: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 9;14:1340452. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1340452. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38264521 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of epidural dexmedetomidine in single-dose combined with ropivacaine for cesarean section.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Apr 8;24(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02519-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38589819 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determination of the Relative Potency of Norepinephrine and Phenylephrine Given as Infusions for Preventing Hypotension During Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Up-And-Down Sequential Allocation Study.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 14;13:942005. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.942005. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910385 Free PMC article.
-
ED50 of ciprofol combined with sufentanil for fiberoptic bronchoscopy of different patient populations with pulmonary tuberculosis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Jun 4;24(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02583-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38834948 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Allen T. K., George R. B., White W. D., Muir H. A., Habib A. S. (2010). A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Four Fixed Rate Infusion Regimens of Phenylephrine for Hemodynamic Support during Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery. Anesth. Analg 111, 1221–1229. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e1db21 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fu F., Xiao F., Chen W., Yang M., Zhou Y., Ngan Kee W. D., et al. (2020). A Randomised Double-Blind Dose-Response Study of Weight-Adjusted Infusions of Norepinephrine for Preventing Hypotension during Combined Spinal-Epidural Anaesthesia for Caesarean Delivery. Br. J. Anaesth. 124, e108–e114. 10.1016/j.bja.2019.12.019 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

