Necroptosis: A Novel Pathway in Neuroinflammation
- PMID: 34322024
- PMCID: PMC8311004
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.701564
Necroptosis: A Novel Pathway in Neuroinflammation
Abstract
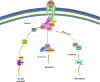
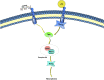
Neuroinflammation is a complex inflammatory process in the nervous system that is expected to play a significant role in neurological diseases. Necroptosis is a kind of necrosis that triggers innate immune responses by rupturing dead cells and releasing intracellular components; it can be caused by Toll-like receptor (TLR)-3 and TLR-4 agonists, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), certain microbial infections, and T cell receptors. Necroptosis signaling is modulated by receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK) 1 when the activity of caspase-8 becomes compromised. Activated death receptors (DRs) cause the activation of RIPK1 and the RIPK1 kinase activity-dependent formation of an RIPK1-RIPK3-mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), which is complex II. RIPK3 phosphorylates MLKL, ultimately leading to necrosis through plasma membrane disruption and cell lysis. Current studies suggest that necroptosis is associated with the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injury. Inhibitors of necroptosis, such as necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) and stable variant of Nec (Nec-1s), have been proven to be effective in many neurological diseases. The purpose of this article is to illuminate the mechanism underlying necroptosis and the important role that necroptosis plays in neuroinflammatory diseases. Overall, this article shows a potential therapeutic strategy in which targeting necroptotic factors may improve the pathological changes and clinical symptoms of neuroinflammatory disorders.
Keywords: mlkl; necroptosis; necrostatin-1; neuroinflammation; ripk1; ripk3.
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Jiang, Su and Zhuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Diaz S., Dillon C. P., Lalaoui N., Tanzer M. C., Rodriguez D. A., Lin A., et al. (2016). The Pseudokinase MLKL and the Kinase RIPK3 Have Distinct Roles in Autoimmune Disease Caused by Loss of Death-Receptor-Induced Apoptosis. Immunity 45 (3), 513–526. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

