Synchronous Small Bowel Gangrene With Pyelonephritis Secondary to Mucormycosis: A Disastrous Complication of COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34322352
- PMCID: PMC8310564
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15911
Synchronous Small Bowel Gangrene With Pyelonephritis Secondary to Mucormycosis: A Disastrous Complication of COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Mucormycosis is a rare infection caused by fungi of the order Mucorales. The infection frequently involves the rhino-cerebral or respiratory system and involvement of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and kidney are rare. It usually infects immunocompromised individuals due to various causes and an upsurge is hypothesized to be linked with irrational use of steroids during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We encountered a rare case of systemic mucormycosis that involved both renal as well as mesenteric vessels and led to ischemia of both vital organs. The patient developed massive bowel gangrene involving the duodenum, proximal jejunum, and left kidney due to angioinvasive mucormycosis. The diagnosis of GI mucormycosis may further increase during the current pandemic. The physicians, as well as surgeons, should be aware of this unwanted complication and keep a high index of suspicion for this rare disease.
Keywords: angioinvasive; bowel gangrene; covid-19; gastrointestinal mucormycosis; vascular necrosis.
Copyright © 2021, Varshney et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
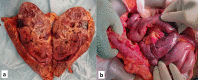
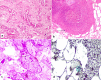
References
-
- The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Jeong W, Keighley C, Wolfe R, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal mucormycosis: an evolving disease. Spellberg B. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22485085/ Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY) 2012;8:140–142. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal mucormycosis in immunocompromised hosts. Dioverti MV, Cawcutt KA, Abidi M, et al. Mycoses. 2015;58:714–718. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
