Genome Instability-Derived Genes Are Novel Prognostic Biomarkers for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34322487
- PMCID: PMC8312551
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.701073
Genome Instability-Derived Genes Are Novel Prognostic Biomarkers for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive disease. Recent studies have identified genome instability-derived genes for patient outcomes. However, most of the studies mainly focused on only one or a few genome instability-related genes. Prognostic potential and clinical significance of genome instability-associated genes in TNBC have not been well explored.
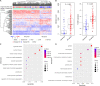
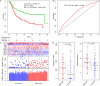
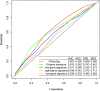
Methods: In this study, we developed a computational approach to identify TNBC prognostic signature. It consisted of (1) using somatic mutations and copy number variations (CNVs) in TNBC to build a binary matrix and identifying the top and bottom 25% mutated samples, (2) comparing the gene expression between the top and bottom 25% samples to identify genome instability-related genes, and (3) performing univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to identify survival-associated gene signature, and Kaplan-Meier, log-rank test, and multivariate Cox regression analyses to obtain overall survival (OS) information for TNBC outcome prediction.
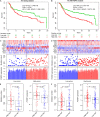
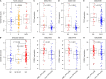
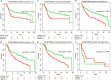
Results: From the identified 111 genome instability-related genes, we extracted a genome instability-derived gene signature (GIGenSig) of 11 genes. Through survival analysis, we were able to classify TNBC cases into high- and low-risk groups by the signature in the training dataset (log-rank test p = 2.66e-04), validated its prognostic performance in the testing (log-rank test p = 2.45e-02) and Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) (log-rank test p = 2.57e-05) datasets, and further validated the predictive power of the signature in five independent datasets.
Conclusion: The identified novel signature provides a better understanding of genome instability in TNBC and can be applied as prognostic markers for clinical TNBC management.
Keywords: TNBC; copy number variation; genome instability; mutation; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Guo and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

