Upregulation of interleukin-19 in severe asthma: a potential saliva biomarker for asthma severity
- PMID: 34322544
- PMCID: PMC8311130
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00984-2020
Upregulation of interleukin-19 in severe asthma: a potential saliva biomarker for asthma severity
Abstract
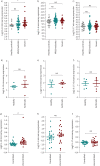
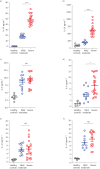
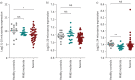
Interleukin (IL)-19, a designated IL-20 subfamily cytokine, has been implicated in inflammatory disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and, lately, asthma. Here, through the analysis of transcriptomic datasets of lung tissue of large asthma cohorts, we report that IL-19 expression is upregulated in asthma and correlates with disease severity. The gene expression of IL-19 was significantly higher in lung tissue from patients with severe and mild/moderate asthma compared to healthy controls. IL-19 protein level, however, was significantly higher in the blood and saliva of patients with severe asthma compared to mild/moderate subgroups as measured by ELISA assay. IL-19 protein level was not affected by corticosteroid treatment in plasma. Our data provide insights into the potential use of IL-19 as a saliva marker for asthma severity and a potential therapeutic target.
Copyright ©The authors 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: F. Saheb Sharif-Askari has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Saheb Sharif-Askari has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Goel has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: B. Mahboub has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.W. Ansari has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M-H. Temsah has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.M. Zakri has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Ratemi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Hamoudi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Q. Hamid has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Halwani has nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
